A look at SAP Fieldglass – Cloud-based Vendor Management System
Primer on SAP Fieldglass
Utilising specialised services and engaging temporary staff are common activities for many organisations. The systems used to support these processes are not often optimal and frequently done manually using tools such as Excel. According to a US government accountability report, nearly 40% of the US workforce consists of external workers. Considering current changes – there is an even greater trend towards wider adoption of an external workforce. SAP Fieldglass is a cloud-based solution encompassing many of the processes involved in engaging such staff & services and provides an efficient way of handling them. It provides for two broad categories of procurement, the first being procuring an external workforce to staff project teams and the second being procurement of services such as advertising, which falls outside the core competency of an organisation.

Terminology
Fieldglass uses certain terminology relevant to this industry and it is imperative to know them to understand the solution:
Buyer is an organisation, which is looking for people with a specialised skill set, who are required to be part of their project team on a temporary basis.
Supplier is an organisation which provides such staff to the Buyer organisation. Typically, supplier organisations specialise in providing a workforce with specific skills such as Architects, Designers and Information Technology professionals.
Worker is a person with specialised skills such as designing, who is engaged to do the work of the Buyer, provided by the Supplier.
Contingent Worker is a term used to mean that the Worker is made part of the Buyer’s Project team under the direct management of the Buyer Organisation. He/she assumes responsibilities and delivers results as part of the Project team. However, this does not mean the worker is a direct employee of the Buyer organisation.
Services Worker is a term used to mean that the Worker is expected to deliver a pre-defined service under a contract, called a Statement Of Work (SOW) with the Supplier organisation. This means the worker is NOT managed by the Buyer Organisation directly.
Programs are a combination of people, process and platform, created by the Buyer organisation to execute and achieve certain organisational objectives.
Program Management Office (PMO) is a department or a group in the Buyer organisation, responsible for managing projects/programs. One of them typically is external workforce management program.
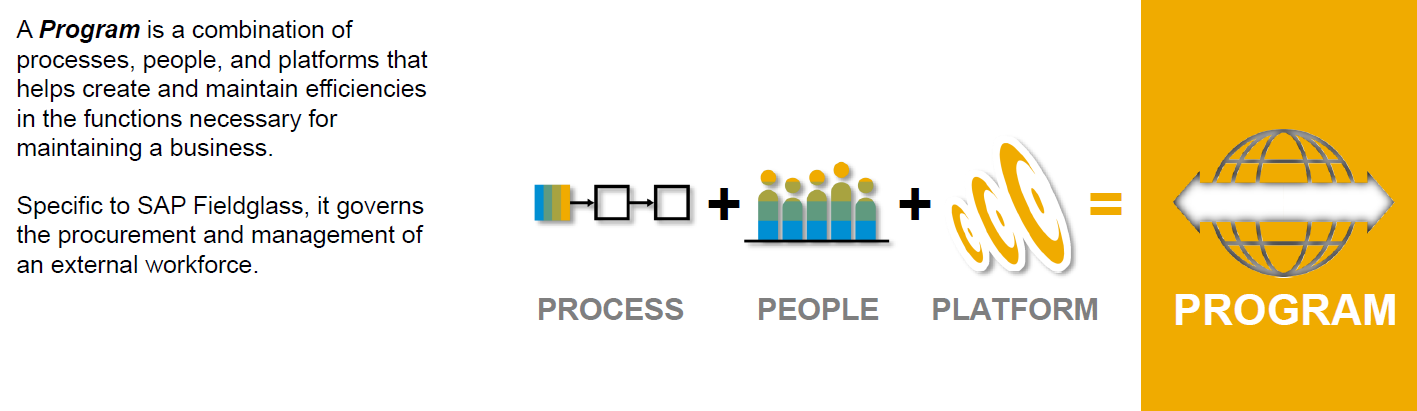
Exhibit-1 (Credits : SAP SE)
The PMO carries certain responsibilities and duties defined by the Buyer organisation. The program of managing an external workforce involves procuring workers at the best possible rates, ensuring a quality worker is provided by suppliers, and that processes for compliance with labour laws and contractual obligation are adhered to (among other things). Exhibit-2 below explains the typical responsibilities of PMO.
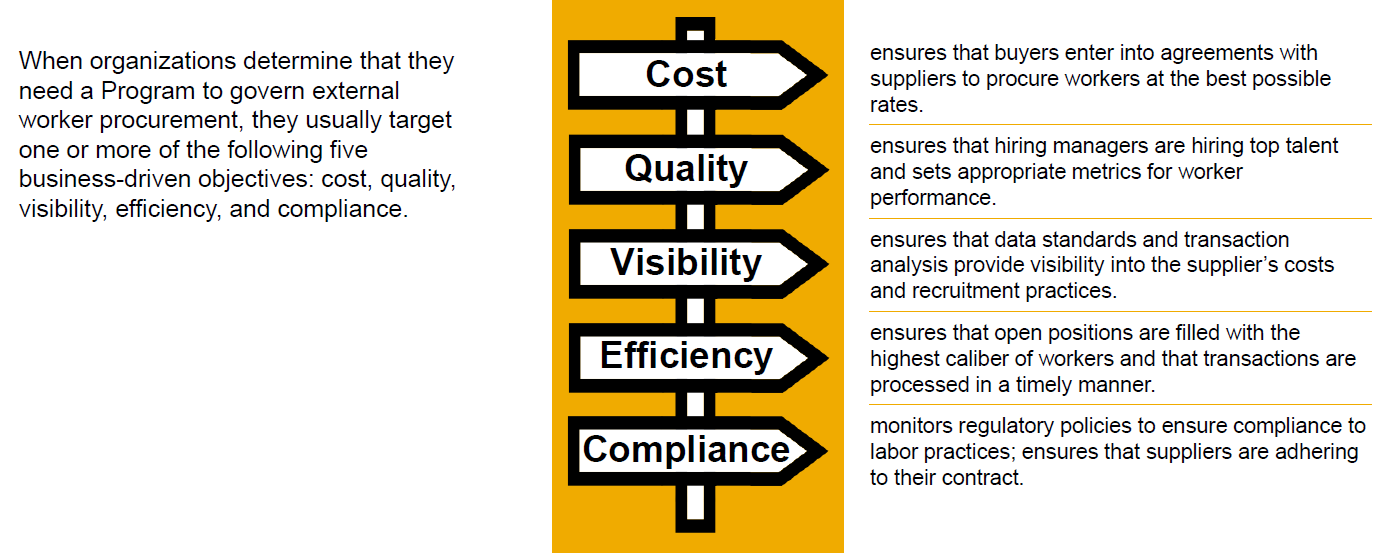
Exhibit-2 (Credits: SAP SE)
SAP Fieldglass Solution
Fieldglass is a Cloud-based Vendor Management System, which allows both Buyer and Supplier to manage the external workforce management. It provides for visibility into voluminous transactions and documents generated during these processes and helps to manage cost, quality and compliance among others. Exhibit-3 below shows in brief the different aspects of the solution in a nutshell.
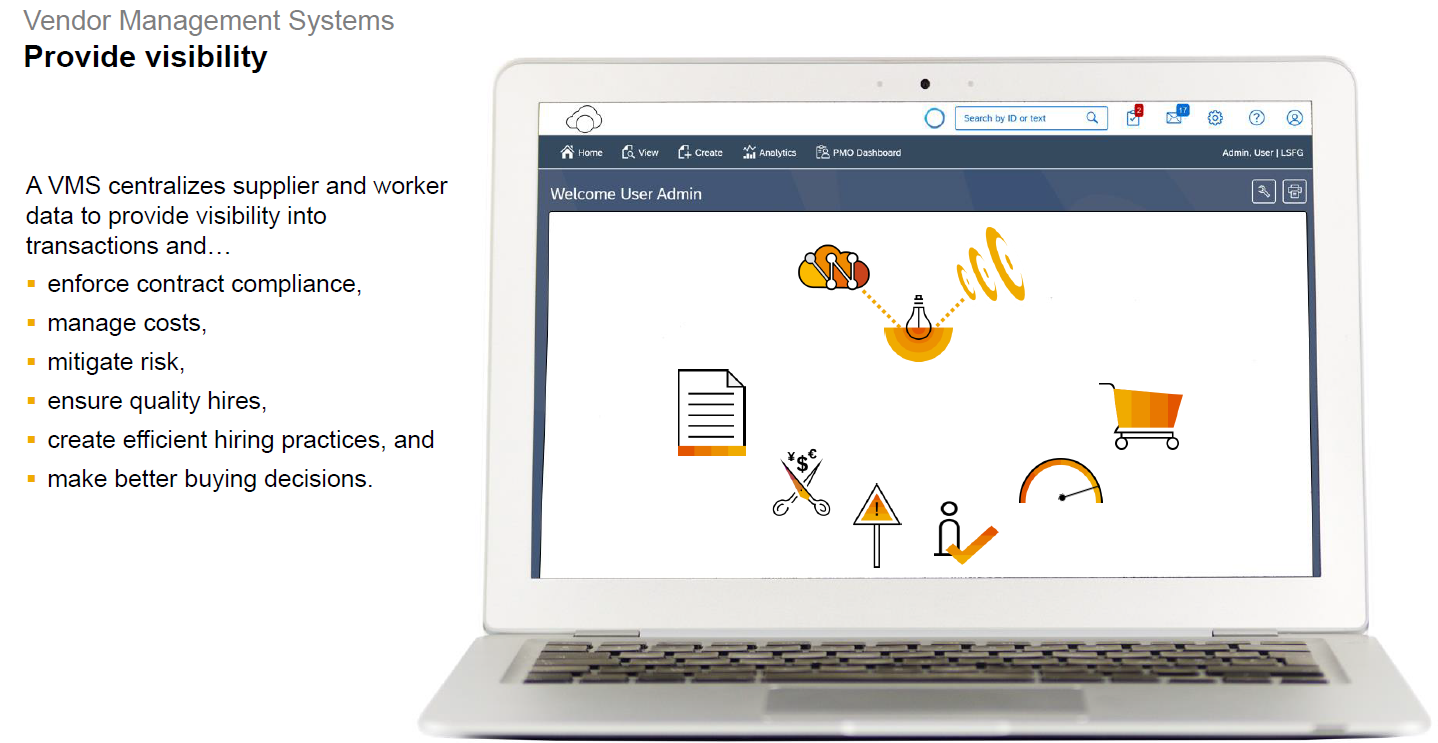
Exhibit-3 (Credits: SAP SE)
SAP Fieldglass Staff Procurement Process
SAP Fieldglass is a configurable solution using an organisations’ own process of contingent worker management and which can be tailored. Each organisation uses Fieldglass and configures its own unique process workflows to suit their needs. Let us look at typical workflow process steps given below, to understand the Fieldglass solution. This is only one of the possibilities, just for us to understand.
1. Buyer creates a “Job Posting”: It is the responsible manager who has the requirements and creates the details as “Job Posting”
2. Approving the Job Posting: Typically, it is the responsible person in PMO who does the approval
3. Distributing the Job Posting: The job posting is distributed via a workflow to eligible Suppliers. They validate potential candidates and submit them to PMO of Buyer organisation.
4. Reviewing Submitted Candidates: PMO reviews and ensures compliance and shares them to the responsible managers
5. Selecting Candidates: The responsible manager conducts interviews and selects the appropriate candidate.
6. Creating Work-order: The responsible manager creates a work-order for the selected candidate.
7. Approving the Work-order: The work order travels on the workflow to PMO and any other approvers as per the configured workflow. The necessary approvers sign-off on the workflow
8. Notifying Supplier: The supplier gets a notification via workflow of the selected candidate
9. Worker Registration: The worker registers his details on the Fieldglass application. After completing an on-boarding process as per the buyer organisation, he/she starts working on the project
10. Track time and Expenses: The worker periodically fills the timesheet and expense claims, and creates other necessary documents and submits for approval
11. Approving Time and Expenses: The responsible manager in the Buyer organisation approves the time sheets and expenses.
12. Generating Invoice: An invoice is automatically generated on behalf of the Supplier and paid by the Buyer organisation
13. Payment to Worker: The supplier in turn pays the worker as per their agreed contractual terms.
The above workflow is explained pictorially in the below diagram, exhibit-4
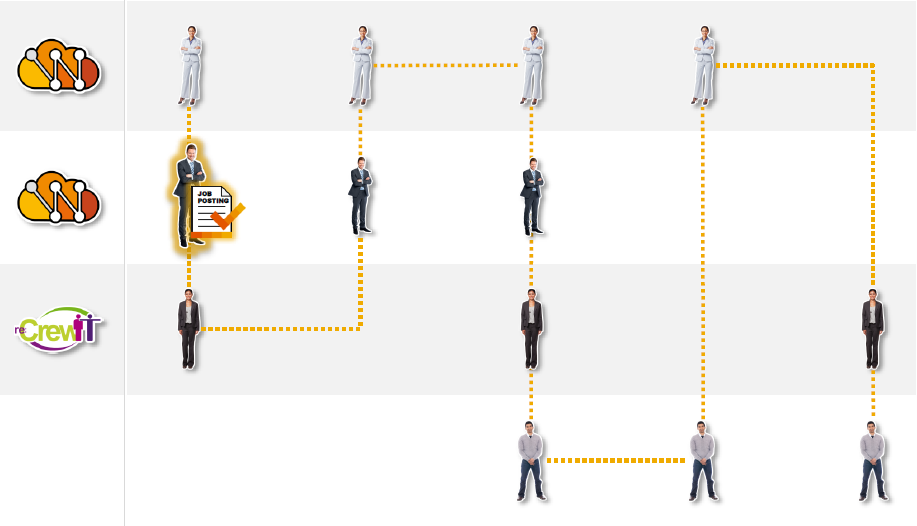
Exhibit-4 (Credits: SAP SE)
Services Procurement
Many organisations prefer to engage external service providers for activities which are not core to the organisation’s business. It also requires specialised skills, management and execution capabilities which may not exist within the organisation. Examples of such tasks are setting up of an additional workspace, launching an advertisement campaign for a new product, designing and creating a new recreational space for the employees, etc.
There are many ways an organisation can engage with such service providers. It depends on the nature of the service – some services may be for a short-term project. For example, setting up of an additional workspace may be an 8-12 week project. Here the service provider may agree to prepare a layout of the seating for employees, organising furniture & lighting, laying electrical wirings, etc and handover a fully functional office space.
Some services are for a medium-term project for 3-6 months. For example, launching to market an organisation’s new product by a marketing company. This may involve studying different markets suitable for the product, the nature/size/timing/channels of campaigns, and collecting feedback from the customers, etc.
Other types of services are continuous in nature. For example, cleaning of office interiors and building, repairs/replacement/upkeep of worn-out electrical and heating systems periodically, etc. This may involve service personnel week on week carrying out these activities on a continuous basis. The buyer organisation may negotiate a contract to pay for these services on a weekly/monthly basis to a service organisation.
The following exhibit 5, depicts the same pictorially.

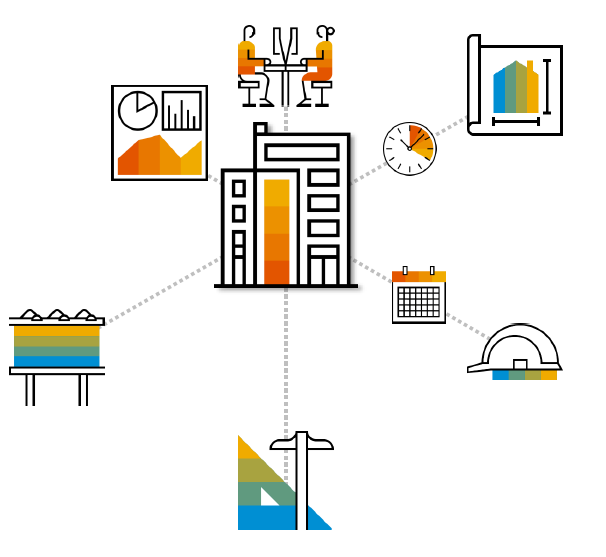
Exhibit-5 (Credits: SAP SE)
Statement of Work (SOW) is the guiding contract for the service provider. The SOW contains all the important aspects of what work will be done, when the work will be started/completed, what are the key deliverables as a result of such work, what should the quality of such services be, and other such things. A key point to observe is that the services delivery is directly governed by SOW terms and the buyer organisation will not have any day-to-day involvement or control of such activities.
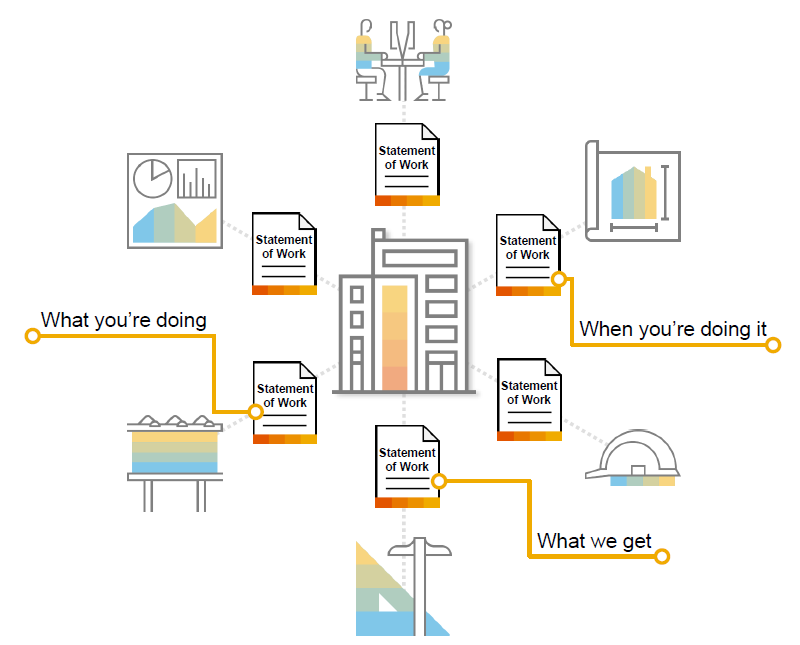
Exhibit -6 (Credits: SAP SE)
SAP Fieldglass Services Procurement Process
Similar to the Staff Procurement process we understood earlier, SAP has provided a configurable solution for the Services Procurement Process. This is typically configured based on each organisation’s needs during the implementation of the solution. Fieldglass provides for different types of SOW’s template creation, which drive the workflow and such other rules. These are handled during the implementation of Fieldglass solution. Let us look at typical workflow process steps in a service procurement process as enunciated below. Again, this is only one of the paths, just for us to understand.
1. Buyer creates SOW: The responsible person creates a SOW in the Fieldglass solution using an appropriate template. Details like tasks, timeline, number of workers, deliverables/milestones, costs are entered in the solution among many other details.
2. Submit SOW to Supplier: A completed SOW is provided to the Supplier, who has been shortlisted for this project. Typically, every organization has a set of shortlisted suppliers and they conduct discussions, elaborating the requirements via a “request for proposal” and request suppliers to provide their responses. Based on their responses, an appropriate Supplier is shortlisted.
3. Supplier review and edits to SOW: Supplier reviews the SOW for its accuracy as per agreed technical/managerial terms, deliverables, costs, timelines, etc . Any corrections and changes needed are updated in the SOW and submitted back to the buyer. There may be many iterations of submissions back & forth between both Supplier and Buyer during this process.
4. Buyer review and finalisation: Buyer reviews the updated version of SOW and makes further edits as necessary. This may be done after discussions, if any are needed with the supplier. The finalised SOW is routed to all the approvers in the Buyer organisation.
5. Approval of SOW: PMO and such other approvers in the Buyer organisation review and approve the SOW.
6. Supplier approval and Workers Addition: Supplier receives the approved SOW and provides their approval. Once it is approved by Supplier, SOW can no longer be altered by the supplier. However, the supplier can add the workers for delivering the services along with further details of their rates and other such information.
7. Buyer approves Workers: Buyer reviews to check it is in line with the agreed terms of discussions and approves the workers.
8. Worker registration: The workers receive notification and they register themselves in the Fieldglass solution. Typically, there are other activities such as badging, background checks etc that are also triggered in the Fieldglass solution (pre-configured during implementation) once registration is complete.
9. Worker submission of time and expense: As the contract progresses, the worker submits the work completed, time spent, expense claims (if any) in the system periodically. This is automatically approved, and an invoice is auto-generated by Fieldglass.
10. Supplier completes milestone: As time progresses, the project reaches the target completion of milestone. The supplier responsible person, updates the completion of milestones, as and when it is achieved.
11. Buyer approves milestone: The buyer gets an appropriate notification and verifies and approves the completion event.
12. Invoice creation and payment: Once approved, an invoice is created automatically by Fieldglass and gets paid to the supplier, as per buyer’s accounts payable system.
Fieldglass also provides for “Profile Worker”. A profile worker is a worker from another organisation who performs certain jobs like cleaning and maintenance work of the building, which is not contracted directly by the Buyer organisation. For example, the Buyer organisation is a tenant in the building and the worker is an employee of the management office of the building. In order to provide access into the buyer organisation and also to track the external person, the buyer organisation creates the profile of the person in Fieldglass.
The above workflow is explained pictorially in exhibit-7 below
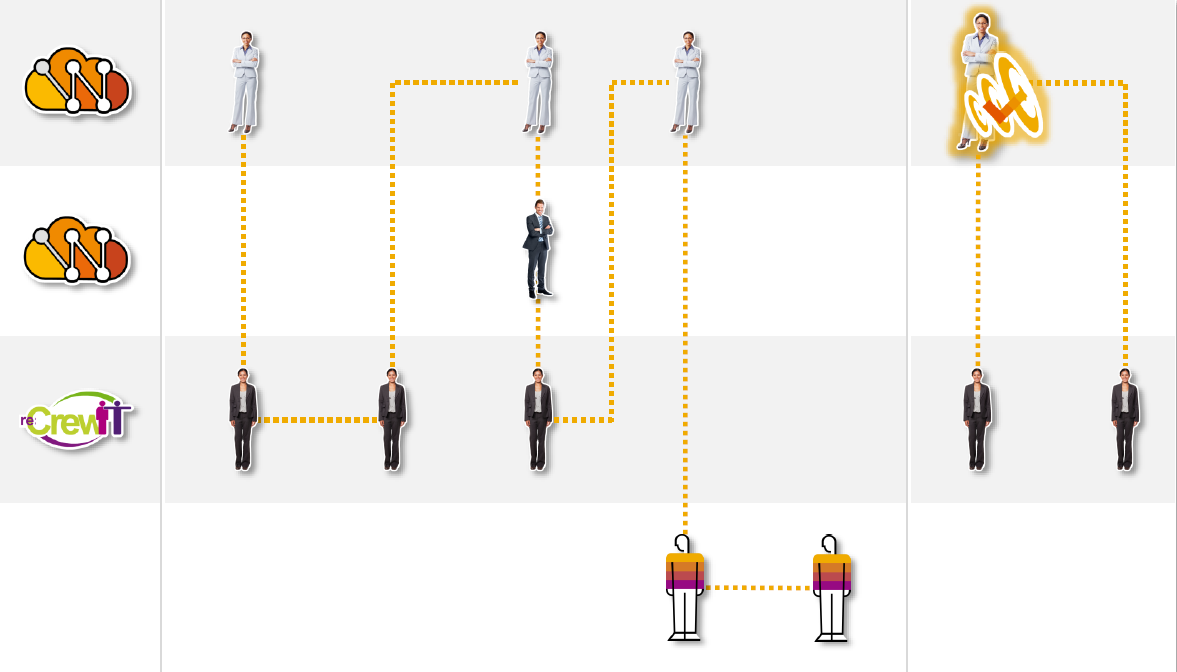
Exhibit-7 (Credits: SAP SE)
Summary
The above gives an overall view of the SAP Fieldglass solution. These are processes followed by many industries engaged in hiring and employing specialised skill workers temporarily, for a specific duration, through the suppliers. In current times, engaging external workers has become imperative for cost optimisation and other such objectives. SAP Fieldglass may be a good opportunity for consultants who wish to retrain themselves in new skill areas, as the usage and demand is certainly on the increase.
Author : Ravi Srinivasan , SAP Alumni
References:
• Fieldglass Homepage
Stay tuned for more insights on Eursap’s Blog…
Need to hire SAP Fieldglass Consultants?
Get in touch with Eursap – Europe’s Specialist SAP Recruitment Agency
