SAP S/4HANA Central Finance (CFIN) Scenarios
SAP S/4HANA Central Finance (CFIN) Scenarios
Introduction
One of the important goals of a finance team, in any organisation, is to publish an annual audited consolidated financial statement to its shareholders in a timely manner. This is the most challenging time for finance teams in any organisation, as many tasks must be accomplished with 100% accuracy within a limited timescale. There were targeted solutions, such as Hyperion, available to organisations to achieve consolidation functions for more than a decade. The growth of business requirements nowadays demands high performance in every function of the organisation almost on a continuous basis. Leveraging better IT solutions and availability of telecom infrastructure, organisations have already moved or are moving into newer operational models such as centralised shared services.

SAP S/4HANA Central Finance (CFIN) is an innovative solution to address organisations’ need for consolidations and centralisation of certain functions on a real time basis. This article helps Solution Architects and Strategy Consultants to have an overview of SAP Central Finance, approaches necessary to adopt Central Finance and new centralisation functions which can leverage Central Finance as a pivot and bring more value to customers.
SAP Central Finance is an SAP S/4HANA system, which can be an independent instance, receiving real time financial transactions via replication servers from SAP or Non-SAP systems. There are many benefits of using Central Finance. It provides real-time planning and consolidation of transactions. It facilitates a scalable local as well as central process execution in a complimentary way to source ERP systems. It helps customers to leverage advanced finance data architecture such as “Universal Journal”.
Many times, organisations have legacy SAP instances, such as SAP ECC or even SAP 4.x, along with non-SAP systems and certain point-solutions. It would be a huge challenge for them to migrate from those systems into SAP S/4 HANA. This is one such situation where SAP Central Finance can help. Let us see the key use cases below.
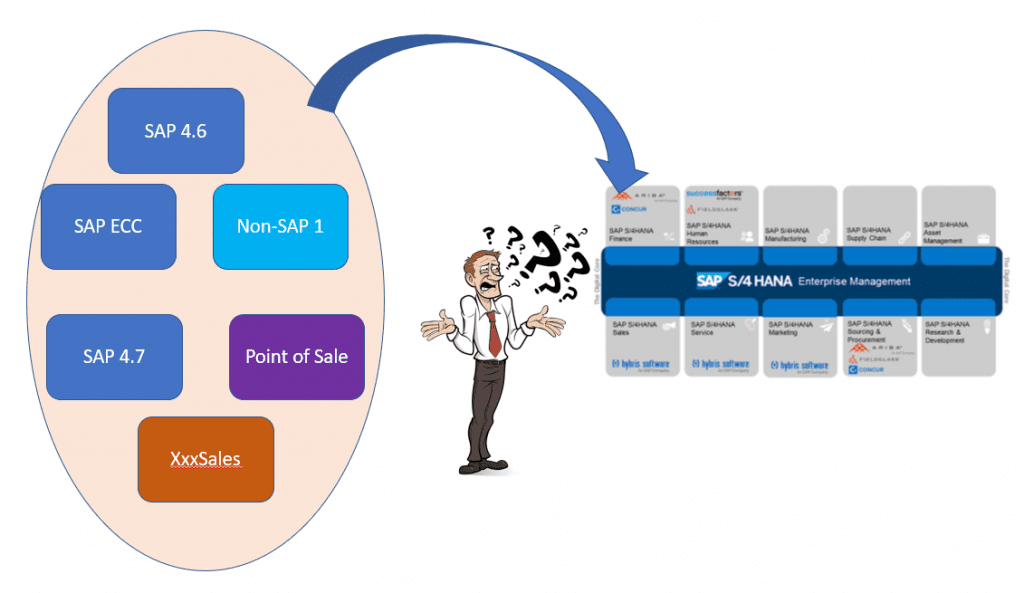
Exhibit -1 (Credits: SAP SE)
Cases for Central Finance:
The following common use cases exist, where Central Finance can bring innovative solutions:
- As a Migration Path to S/4 HANA
- To Centralise Processes across the organisation
- During Reorganisation and/or Mergers
- For Corporate Consolidation and Reporting
As a Migration Path to S/4 HANA:
The current customer landscape has many instances of SAP and Non-SAP solutions. The cost and effort involved are huge in completing a Business Process Re-engineering exercise study and implement a unified solution to replace all the “island solutions” using the “Big Bang” approach. However, competition in the market does not provide the organisation with enough time or resources to undertake such a massive exercise. It is imperative to adopt innovations available in S/4HANA in a quick and agile manner to stay in the market and gather momentum to build an intelligent enterprise. Keeping existing instances and systems as they are, a standalone green field implementation of SAP S/4HANA Central Finance is done at corporate head offices. By establishing the necessary connections from existing instances/systems, real-time data flows into Central Finance for selected finance, accounting and business planning scenarios. This helps the team to achieve quick results, learn S/4 HANA architecture and innovations “on-the-go” and back-work on how to re-engineer existing processes. This acts like a Proof of Concept in real time, specific to their environment. This approach helps organisations to gain knowledge & time and plan the migration of existing systems to S/4HANA in a phased manner.
To Centralise Processes:
Geographically spread organisations have typically decentralised operational functions, such as AR, AP, GL at each of these locations, when operations initially began. Advances in IT and telecommunication infrastructures enable organisations to centralise and optimise certain processes, for example cash management, liquidity management, vendor payment processing, payroll processing etc… This is typically done by establishing “Shared Service Centres”, which handles these processes for all the locations, which in turn leads to cost efficiencies and faster processing times. Again, keeping the existing instances as they are, a green field Central Finance instance implementation can help establish a “Shared Service Centre” within a short period of time. It also helps organisation to move in phased stages to SAP S/4HANA.
Due to Reorganisation and/or Mergers:
Business needs can cause organisations to forge alliances with other organisations or at times to reorganise their existing operations, for example, divide into different verticals. When there are mergers and acquisitions, different IT systems must be consolidated. Central Finance can connect with these systems for process integration and show the consolidated financial data without disrupting existing IT systems. However, it is dependent on many factors specific to each situation.
For Corporate Consolidation and Reporting:
Large corporations with multiple subsidiaries or multiple manufacturing/sales locations have a need to consolidate their financial results periodically for controlling & statutory and legal regulatory compliance. Collecting data and consolidating is a very time consuming and error prone activity. Central Finance instance can connect with a multitude of systems with ease and provide the necessary control and timely accurate data.
Let us look (below) at some of the new centralisation functionalities which can leverage Central Finance as the pivot and bring more value to customers.
1. Centralised Payments:
The central payment function in SAP Central Finance helps an organisation to make payments from central locations, typically corporate headquarters, and perform centralised clearing activities rather than having to do this in different locations. This functionality is activated per company code. Once activated, invoices posted in the source systems are technically cleared and replicated to the Central Finance system and paid there. Related to this is Credit Management, which can also be activated in Central Finance. If done, credit checks are triggered in the local system (at sales order entry) and carried out in the Central Finance. Cash and Liquidity management can also be activated in the Central Finance system. This is an important function for achieving efficiency in funds management, typically a requirement in many large companies. More information on Cash Operations is available in this earlier SAP Cash Management Blog post . More information relating to the activation of Central Payment can be found in SAP Note: 2346233.
2. Group Reporting
“Group Reporting” is a component of SAP S/4HANA. This component provides functions for management reporting, group accounting by supporting processes for data quality control, consolidation process control and reporting. The application component in SAP is – FIN-CS (SAP S/4HANA for Group Reporting). This works also with SAP Cloud Platform and SAP Analytics Cloud.
Assuming Central Finance is implemented, Group Reporting using this as the data source. Group Reporting has a feature to generate “consolidation org units” based on units in the transaction. Group method of balance sheet valuation/currency conversions, and posting them as manual journal entries, are supported. It also has functions for intercompany elimination of payables/receivables etc… are part of the functionality provided in group reporting. It is also possible to create hierarchies for master data specific to consolidation. This component leverages “Universal Ledger” as a single source of truth. More information relating to group reporting is available in here.
3. Third Party Systems Integrations:
In a Heterogenous Landscape, transaction data from third party systems can also be used to create entries in Central Finance. This enables the Corporate Head quarters to pull data from SAP and Non-SAP systems for consolidation and Group reporting. This is typically achieved by using an SLT architecture as shown in exhibit -2 below.
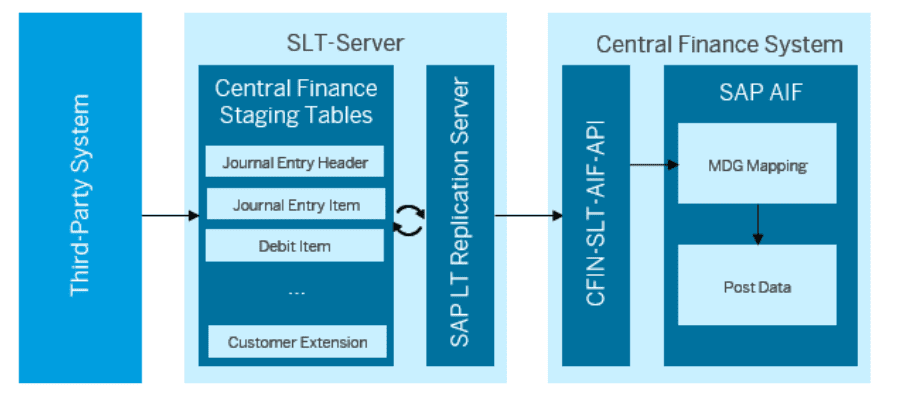
Exhibit-2 (Credits: SAP SE)
Extracting data from Non-SAP systems, and loading them into SLT Staging tables, must be a separate exercise, handled by customer experts on Non-SAP systems. Once this is accomplished, replication from SLT to Central Finance will follow SAP process. To check the FI documents posted from third party systems, one can use programs FINS_CFIN_DFV_FI_NUM (Header) and FINS_CFIN_DFV_FI_DOC (Line items). SAP Note: 2610660 provides information on this topic.
Summary:
SAP Central Finance is much more than a consolidation system if leveraged properly. In the 1809 release, SAP has provided many more functions to support Centralised Project (WBS) reporting, Commitment Management (from Purchase Requisition/ Purchase Order) and Down Payments. SAP Architects and Strategy Consultants can certainly bring out much more value, by looking at customer landscapes and requirements and creatively leveraging Central Finance to achieve efficiencies. It is an exciting new area and the sky is the limit for you to bring value to customers in a non-disruptive way!
References:
SAP Model Company for Finance 1809
SAP Central Finance- Basic Setup and Configuration
Author : Ravi Srinivasan , SAP Alumni
Need to hire SAP S/4HANA CFIN resources?
Looking for SAP S/4HANA CFIN work?
Get in touch with Eursap – Europe’s Specialist SAP Recruitment Agency
