A Quick Look into Some of the Key Concepts and Capabilities of SAP HANA Cloud
Primer on SAP HANA Cloud
SAP HANA has been familiar terminology for all SAP Customers and SAP Eco-system players for the past few years. The search and innovation for a faster and lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) resulted in SAP HANA In-Memory database between 2000 and 2010. SAP HANA (typically in On-Prem systems) started replacing the traditional relational database in SAP systems. Further technological development in the last decade – such as Cloud Computing and Infrastructure as Service – have matured into robust operating platforms. Leveraging these developments, SAP has come out with SAP HANA Cloud as a “Database-as-Service” offering.
In this blog we will briefly look into some of the key concepts and capabilities of SAP HANA Cloud.
SAP HANA Database
Consists of Application Development Capabilities, Smart Multi-Model Processing abilities, Data Virtualization possibilities and database management tools. On the Application Development side, it supports multiple languages, standards like SAP UI5 and complete application life-cycle management capability. Apart from handling columnar database, handling geo-spatial queries (e.g. how many customers are within a 3 km radius of this store), graph analysis, documents to store unstructured data (e.g. external JSON data) and other features are part of Smart Multi-Model Processing. On the Data Virtualization, data caching or data replication or federating data from other systems are other features that are in-built. On the data management side, it has features of multicore and parallel processing, multi-tenancy, multi-tier storage and many other similar high-end capabilities. It is pictorially depicted in Exhibit-1 below.
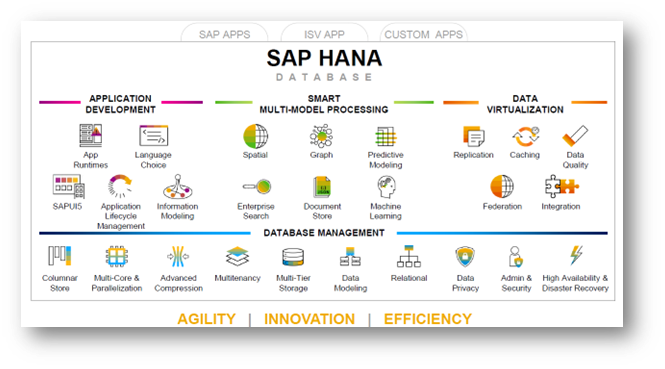
Exhibit-1 (Credits : SAP SE)
SAP HANA Deployment
SAP HANA can be deployed On-Prem, Cloud or Hybrid models. SAP has already tested and certified many Cloud Providers like Amazon/Microsoft/Google for their compatibility. This helps give flexibility to customers and avoid the service provider lock-in challenges. Any development on the SAP HANA can be deployed to multiple cloud systems simultaneously. Customers can also leverage the Cloud Service Provider’s native services if they need to. This helps customer with enormous flexibility to choose a best path appropriate to their needs. This is explained in Exhibit-2 below.
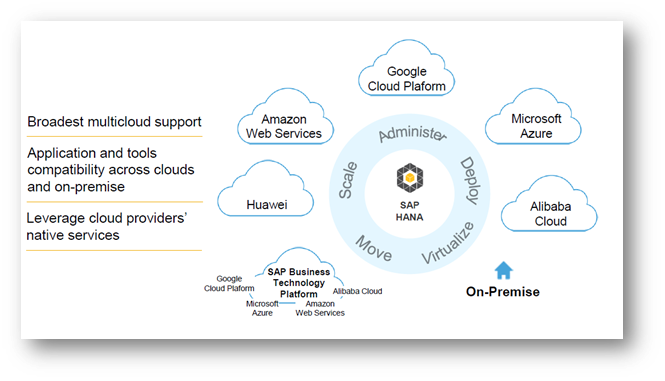
Exhibit-2 (Credits: SAP SE)
On-Prem Deployment Options:
The following two choices are available to customers for On-Prem Deployment:
1. SAP HANA All-in-one Appliance
2. SAP HANA Tailored Data centre Integration (TDI)
In the first choice, SAP has certified combo box of Application, Server, Database, OS and storage as a package. The customer can start the work, just out of the box, for a very fast implementation.
In the second choice, the customer can work with SAP to identify the best possible choices that would work with their existing systems, with necessary flexibility and openness built into them. It helps customer to save IT budget and their existing investments. This is explained pictorially in the diagram below.
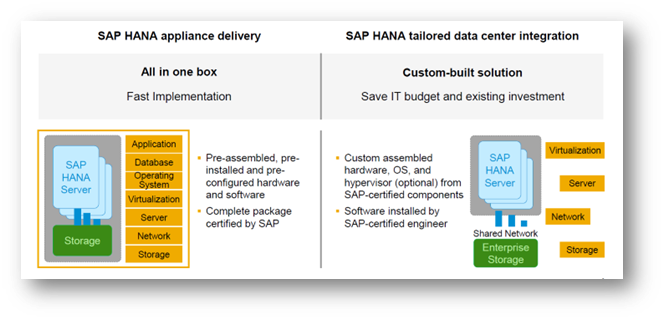
Exhibit-3 (Credits: SAP SE)
On Cloud Deployment Options:
Customers can choose one of the following models for deploying SAP HANA:
• Deploy in Public Cloud
• Deploy in Managed Private Cloud
• Consume Database-as-Service
The individual characteristic of each model is summarised in the table below.
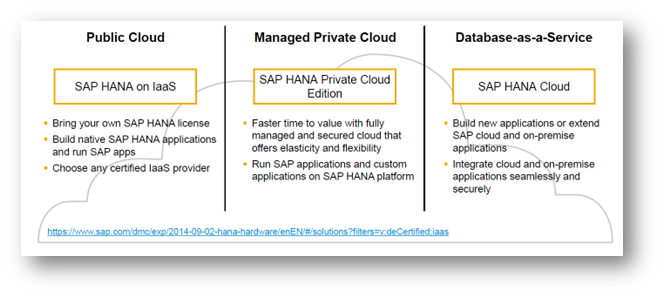
Exhibit-4 (Credits : SAP SE)
SAP HANA Cloud Integration
A key capability of SAP HANA is to integrate data from various sources, irrespective of whether the source is on-prem or on-cloud. The following two concepts are supported in SAP HANA Cloud:
• SAP HANA Smart Data Access referred as SDA
• SAP HANA Smart Data Integration referred as SDI
Smart Data Access – SDA
This concept is also called Data Virtualisation technique. The live data in the remote systems are accessed using the concept of Virtual tables in SAP HANA. Virtual tables are a place holder and pointer mechanism to the remote system where the actual live data resides. The advantage is the programs can be developed without bothering about the systems and locations where the data resides. This is a simple and easy way to “instantly access” any data of the organisation residing anywhere in the landscape. Technically, not even special syntax is needed to access data, when virtualisation is implemented. This is a cost-efficient way to access data for many use cases such as real-time operational reporting, monitoring key performance indicators and predictive analysis for analysing expected results. Pictorially, it is depicted in exhibit-5 below.
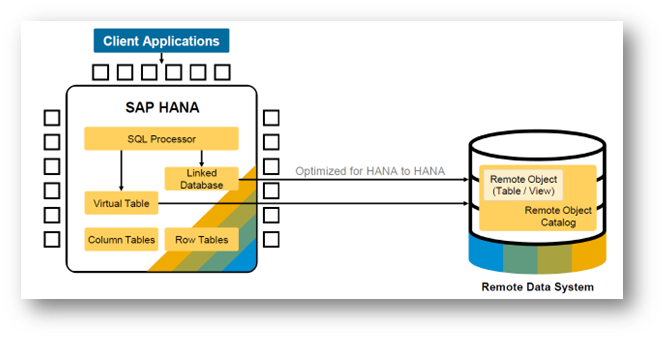
Exhibit-5 (Credits: SAP SE)
The SDA guiding principle is to minimise the data transfer volume between remote systems and Core SAP HANA. This is achieved by remote query execution and transfer only of the results. There are many other optimisation techniques used in SDA, which are summarised in the graphical diagram shown below.
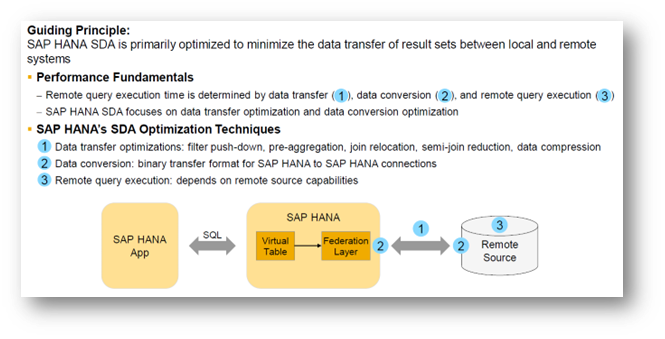
Exhibit-6 (Credits : SAP SE)
Smart Data Integration – SDI
SDI is based on data replication and data transformation services to move data from other systems into HANA. The “native” integration capabilities can handle Bulk/Batch mode data transfers and real time replication from other systems to HANA. The data can come from On-Prem/Cloud/Hybrid data systems. SAP has provided out-of-the box adapters for common sources (like SAP Systems) and also open SDK for customers/partners to build custom adapters. Exhibit-7 below shows a glimpse of databases, files, systems supported by SDI.
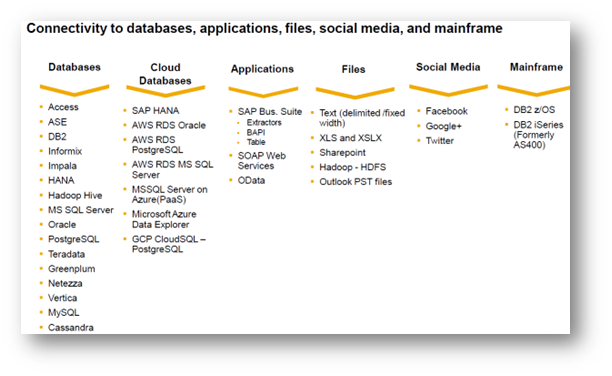
Exhibit-7 (Credits: SAP SE)
Data Provisioning (DP) Agents play a key role in moving data from different systems to HANA. SAP HANA Cloud/Database has an inbuilt DP Server. DP Agent is configured to communicate with DP Server using JDBC/ HTTPS and similar secure protocols. This means, there is no need for VPN/Proxy or other firewall exceptions. Exhibit-8 shows an example of a hybrid integration landscape.
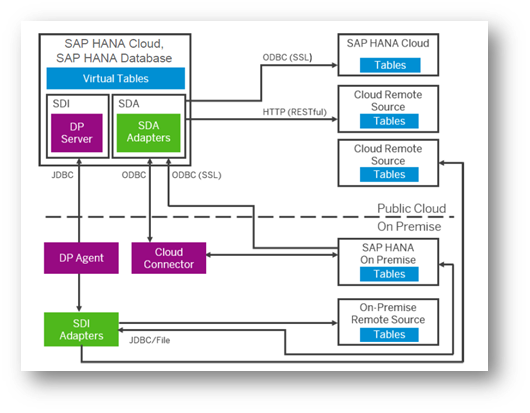
Exhibit-8 (Credits: SAP SE)
SAP has provided a graphical UI to create “Flowgraphs”. For Batch Mode data transfers, users can create, modify, and execute them in an easy way without having to do extensive development. The Real-time data transfers can be configured in a much simpler manner without having to even resort to Flowgraphs – just by selecting source, target, replication behaviour and other such parameters. Below is a sample flow graph and other capabilities.
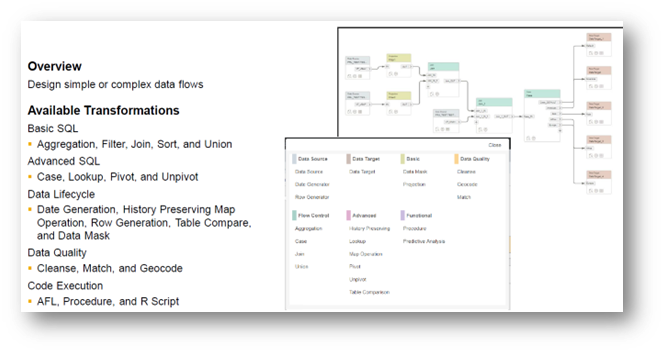
Exhibit-9 (Credits: SAP SE)
Typically, in a heterogenous system landscape, whenever data is aggregated into another system for reporting/further processing, data invariably must be cleaned and sometimes morphed to align with other data/masters. As part of SDI, a Data Cleaning service is offered in the cloud on a pay-per-use model. Integrating Data cleaning as part of data movement is very easy to configure from SQL Console by establishing connections and consume microservice. The following diagram shows a snapshot of Data Cleaning microservice.
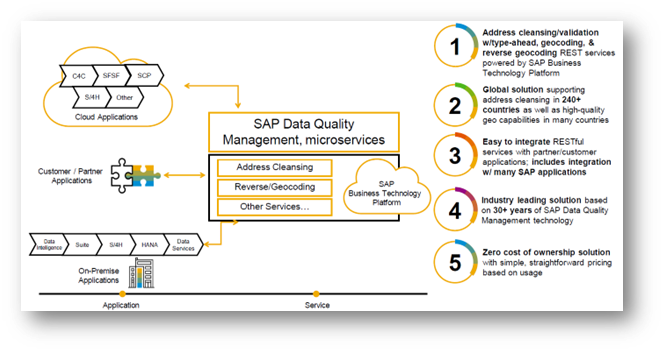
Exhibit-10 (Credits: SAP SE)
Summary
There are many other concepts and tools which SAP HANA Cloud supports. For example, concept of data lake and connectivity to handle less frequently used data is a very useful capability for any growing customer. SAP also offers a “Free-tier” model for SAP HANA Cloud and suite of Business Technology Platform services. This is a great way for organisations to experiment and seamlessly move into a paid model (Cloud Platform Enterprise Agreement [CEPA]). Business Application Studio is another tool for developers supporting both high level coding and graphical Low Code/No Code based developments. In summary, SAP HANA cloud is a treasure trove of tools and concepts, readily usable by both developers and functional consultants.
Author : Ravi Srinivasan , SAP Alumni
References:
• SAP HANA Cloud- Home Page
• SAP HANA Cloud- Free Tier Access
• Certification Link
• SAP HANA Hardware Directory
• What is new in SAP HANA Cloud
• Smart Data Integration-YouTube
• What is Multi-Model Database
