Embedded and Cloud OData Services for SAP Business Suite
Embedded and Cloud OData Services for SAP Business Suite.
Introduction
Open Data Protocol (OData) has become the standard protocol for releasing data stored in SAP Business Suite applications and making it available for user-centric consumption on any device. OData can be easily consumed by various platforms and it offers flexibility (filtering, query options). OData for SAP comprises OData and SAP annotations.

While the SAP HANA application server can publish OData natively, classic SAP Business Suite applications are reliant on SAP Gateway OData services to extract data from back-end systems. SAP Gateway is an on-premise product (ABAP based) that offers capabilities to expose SAP Business Suite functionalities as OData services, which can then be consumed in various user-centric scenarios. It is best suited for SAP Business suite customers who want to bring their SAP business software into new experiences on devices or within rich internet applications.
SAP Gateway has two components:
1. Backend Provisioning Component (IW_BEP):
This component resides on SAP Business Suite and is meant for building the OData services from data sources like RFCs BAPIs etc. Using “Service Builder” tool (transaction SEGW) one can define OData model and corresponding logic for various OData operations (GET, PUT, POST etc.).
2. Gateway Hub:
Once these services are designed using IW_BEP, we need a way to publish and expose them as OData services. This is done using Gateway Hub. Gateway HUB and IW_BEP components communicate via OData Channel or ODC (SAP proprietary) protocol.
There are three practical strategies regarding OData service deployment:
1. Embedded Deployment
As of SAP NetWeaver 7.4 and higher, the core component for SAP Gateway Foundation, SAP_GWFND, is installed as standard. If multiple SAP Business Suite systems are used, SAP Gateway has to be configured for each system.
2. Central HUB Deployment
SAP Gateway also exists as a separate on-premise product. In this case the SAP Gateway server functionalities are only used on one dedicated front-end server, the hub system. That adds one more system in the landscape and increases total cost of ownership. For example, a separate installation of Gateway HUB can be chosen due to security considerations (you can locate the SAP Gateway system in a demilitarized zone).
The SAP Gateway content implementation cannot use most development objects in the SAP Business Suite backend system. Consequently, you need to create copies of structures and data domains, for example. So, even if we choose a separate front-end server as SAP Gateway, it is better to implement and register services in SAP Business Suite with Backend Provisioning Component, and then publish them on the SAP Gateway server.
3. OData provisioning
In many respects, it is like Central Hub deployment strategy. The main difference: the SAP Gateway frontend part will be managed by SAP cloud platform.
OData services are connected to HANA cloud via a cloud connector (a secure way with several authentications before connecting to backend systems).
The cloud connector runs as on-premise agent in a secured network, and acts as a reverse invoke proxy between the on-premise network and SAP HANA Cloud Platform. Due to its reverse invoke support, you don't need to configure the on-premise firewall to allow external access from the cloud to internal systems.
Another benefit for using cloud is that we can use cloud version of Web IDE (SAP recommended integrated development environment) and reduce the cost and complexity involved in setting up the infrastructure for a development environment. In that way, we can always use the latest features of SAP Web IDE without any installation effort.
Developers access the tool via a browser, so no installation is required, and the configuration is centralized and done only once for all developers in your organization. As the development is done through a browser, you can code anywhere.
The Service Creation Process consists of three phases:
• data model definition
You define the required artifacts such as entity types, entity sets, associations, and other components that your service will use. After data model definition, you must generate the repository objects and register them in the SAP Business Suite system so that you can proceed with the next main phase, service implementation.
• service implementation
In service implementation phase, service generation is the quicker approach than service development and requires a lot less effort. On the other hand, it is more limited, and thus is primarily recommended for developing very straightforward services.
For service generation, if you use data source mapping, service implementation takes place by mapping the OData model to the methods of an RFC function module, search help, or CDS view.
• service maintenance
The service maintenance phase primarily consists of the service activation and service registration step in the SAP Gateway Hub system. The registration and activation of services in the hub is performed using Transaction /IWFND/MAINT_SERVICE (Activate and Maintain Service). Gateway exposes services via HTTP, therefore the Gateway services must be activated on the NetWeaver ABAP system. As HTTP services are run by Internet Communication Framework (ICF), they represent a security risk because they can be accessed directly by the HTTP protocol from the Internet. You therefore need to use suitable methods for restricting access, for example, only permitting access to the ICF service for users with the appropriate authorizations. Also apply HTTPS configuration according to note 1896961 - HTTP/HTTPS Configuration for SAP NetWeaver Gateway.
As already mentioned, we create OData services in the SAP Business Suite by using Backend Provisioning Component (IW_BEP). The most flexible way for creating service is ABAP development, but it also requires some significant technical know-how.
Another way for creating service is service generation. It is the quicker approach that requires a lot less effort. Less experienced developers will appreciate the possibility to use tools that generate OData services without having to write a single line of code.
From SAP ABAP NW 7.50 and above it is possible to develop OData services using service development and the mapping of data sources. This way, customers will be able to leverage their existing resources such as ABAP classes and RFC function modules when using SAP Business Suite EHP 8 or higher or when using SAP S/4HANA on-premise.
The Service Builder (transaction SEGW) allows for centrally displaying and creating the definition of an OData service. This includes runtime artefacts (model provider class [MPC], data provider class [DPC], model, and service), OData artefacts (entity set, entity type, and properties), as well as data sources and models.
It is worth mentioning that we can easily use services generated from SAP BW Easy Queries. For a given SAP BW Easy Query, the system automatically creates an adequate RFC module and generates service based on it. We can add generated service in the Gateway system (transaction /IWFND/MAINT_SERVICE).
Demo Services - a short case study
As a simple and quick case study, I generated two demo services and deployed them in an embedded way. For each service, I used a different service generation technique. The services are:
• service for CUSTOMER_DSO_CALCULATION function module
The Day Sales Outstanding (DSO) analysis is concerned with customer payment history within a specific period and indicates the average number of days that a company takes to collect outstanding receivables, i.e. revenue after a sale has been made. If you have too much credit sales, you are basically giving your customers an interest-free loan, which can negatively affect your cash flow. I used the Service Builder (transaction SEGW) for importing entity type from function module data source and mapping the read method of an entity set to that data source.
• service from Core Data Services (CSD) view ZCDS_PURCH_ORDER_ITEMS
Created with Eclipse and generated with just one magical annotation line @OData publish:true, without the need of Service Builder.
With CDS, data models are defined and consumed on database server rather than on application server. CDS also offers capabilities beyond the traditional data modelling tools, including support for conceptual modelling and relationship definitions, built-in functions, and extensions.
Originally, CDS was available only in the design-time and runtime environment of SAP HANA. Now, the CDS concept is also fully implemented in SAP NetWeaver AS ABAP, enabling using CDS for new SAP Business Suite developments. You can finally define and consume your data models in the same way (syntax, behaviour, etc.), regardless of the SAP technology platform (ABAP or HANA).
From SAP ABAP NW 7.50 and above, you can expose ABAP CDS view as OData service by using @OData.publish:true annotation. As soon as the OData service is activated in the SAP Gateway hub, it is ready for consumption through an OData client, such as an SAP Fiori app.
Prerequisites
1. Install Eclipse IDE and ABAP Development Tools from SAP Development Tools.
2. Activate the Gateway service of the SAP Business Suite system on each client we need (also called “Embedded Deployment”). SPRO -> SAP Customizing Implementation Guide -> SAP NetWeaver -> Gateway -> OData Channel -> Configuration -> Activate or Deactivate SAP NetWeaver Gateway.
3. In the ERP Backend system in transaction SICF the following default_host nodes must be activated: sap/iwbep, bc/adt, bc/webdynpro/wdy_aie_vd_preview, sap/public/opu, sap/opu/odata.
4. You have activated your HCP account (You can get a free trial here).
Embedded Service for CUSTOMER_DSO_CALCULATION function module
By using Service Builder (transaction SEGW), we create project ZCUST_DSO.
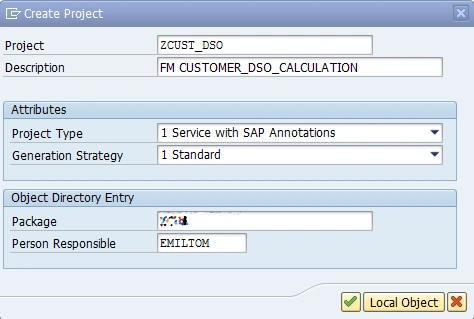
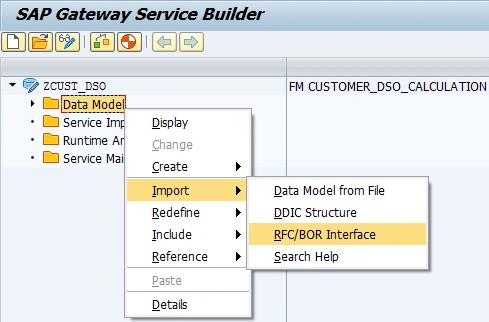
We import entity type from the function module data source.
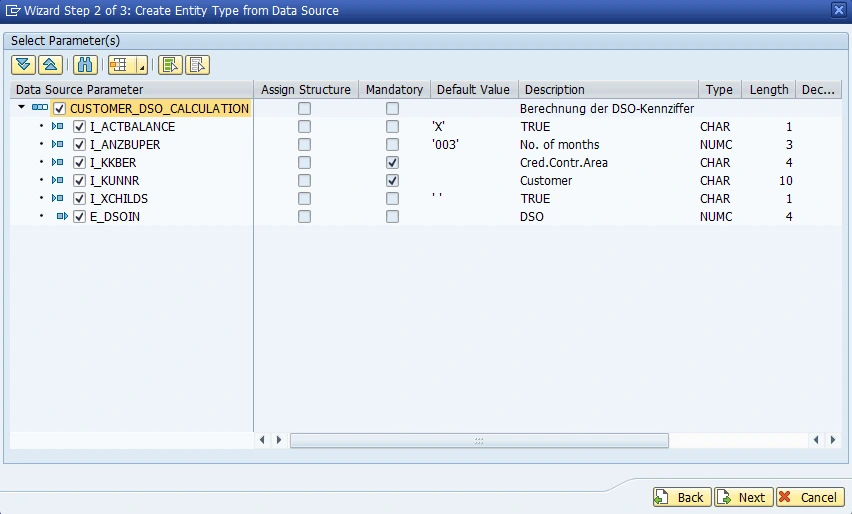
For all data source parameters except E_DSOIN (which is our return value) the check box "Is Key" needs to be checked.
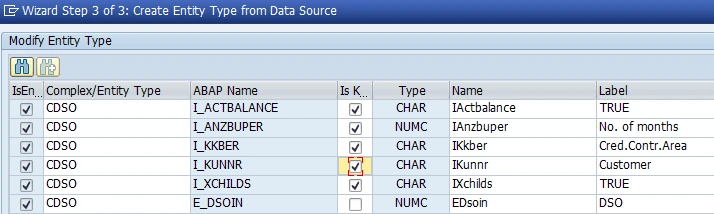
Then we need to map the read method of an entity set to data source. When the service is generated, the GET_ENTITY method is implemented to get details of a single entry in the EntitySet. We pass the key EntitySet properties and get back to single entry.
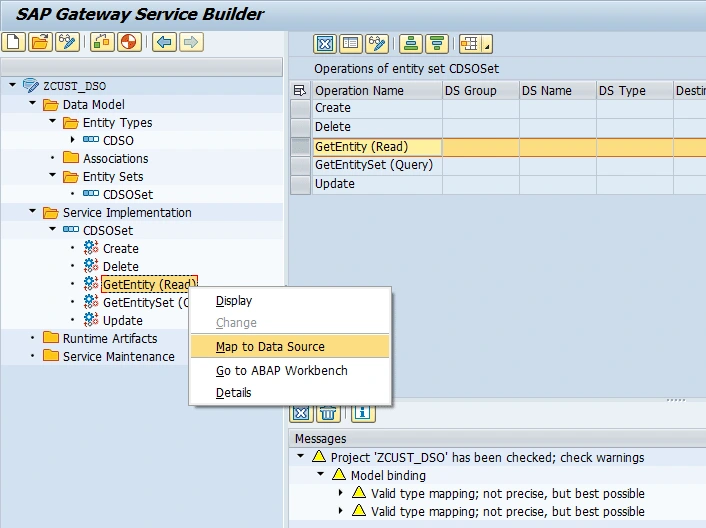
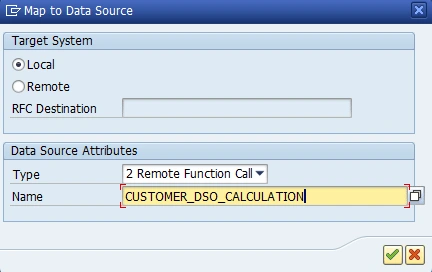
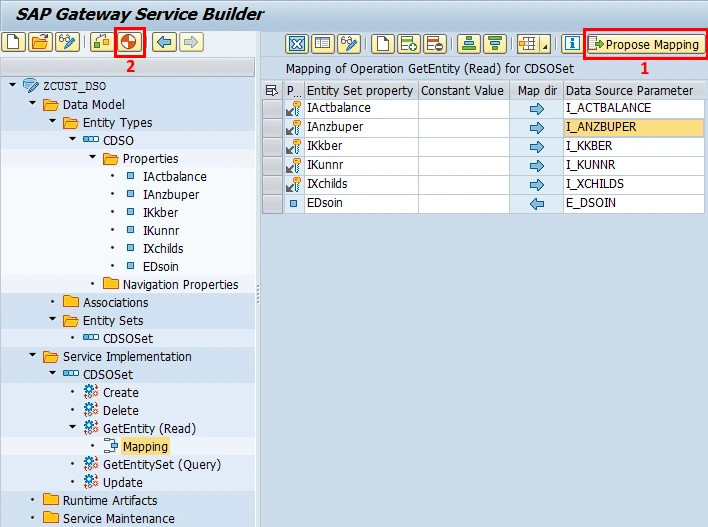
We set input and output mapping directions by clicking to Propose Mapping, and after that we click Generate Runtime Objects button.
We create a new workbench request.
In the end, when calling OData service, I got an error notification because of empty User Name field in the service's assigned system alias entry. The problem is described in the SAP Note 2527329 - No System Alias found for Service < service name > and < current user >.

OData Cloud Provisioning for ZCUST_DSO Service
Cloud to on-premise connection is done via SAP Cloud Connector.
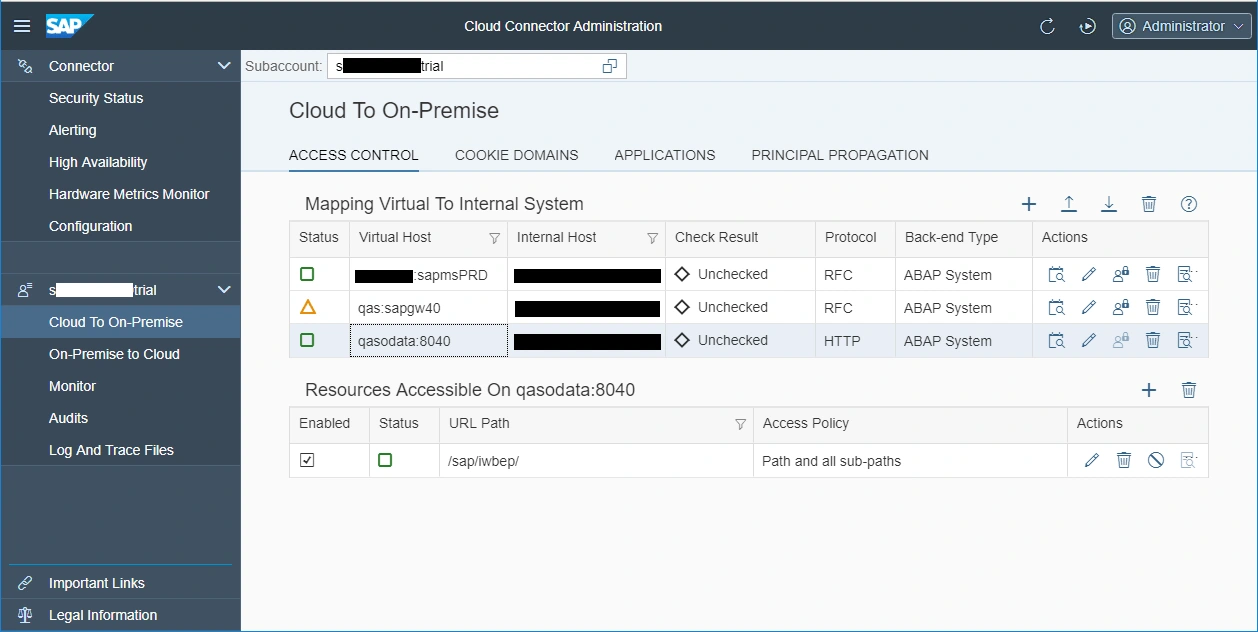
We must enable and configure OData Provisioning service in SAP Cloud Platform Cockpit.
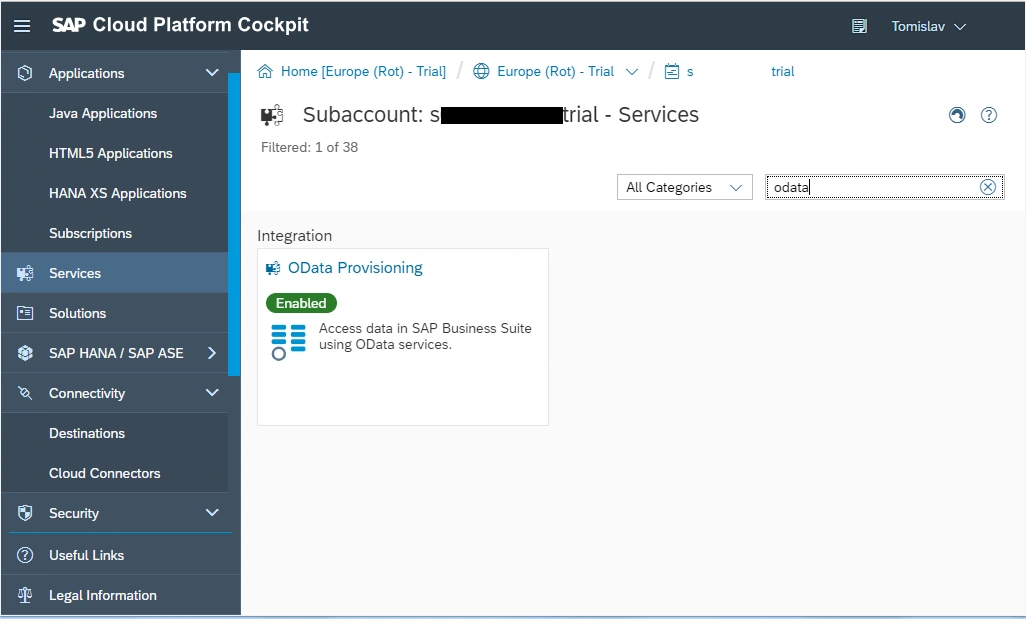
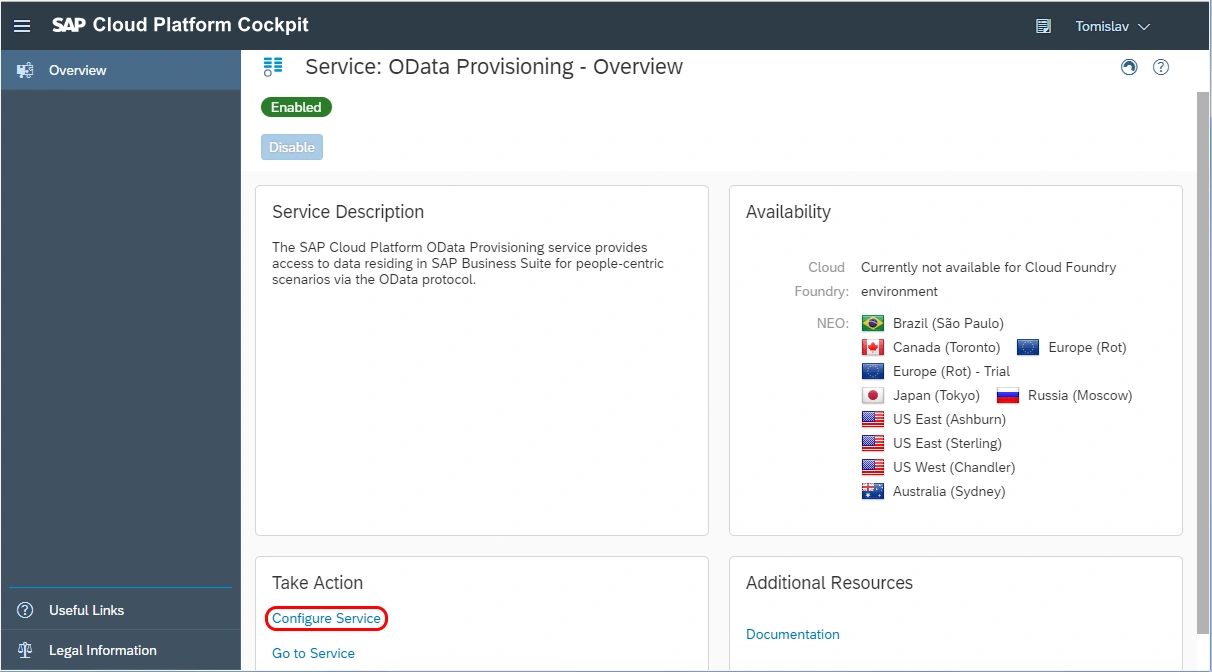
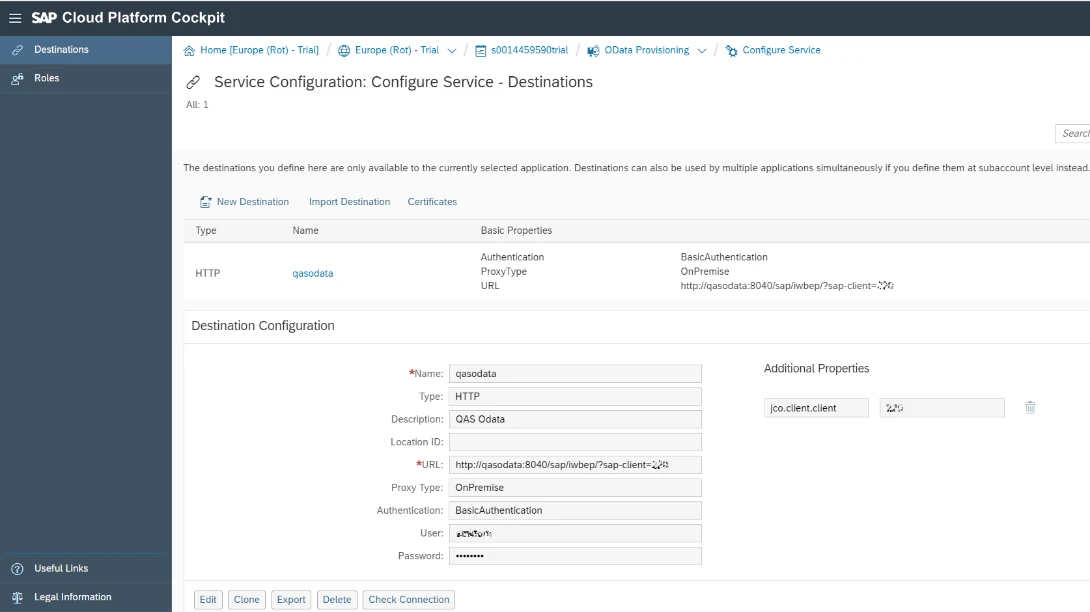
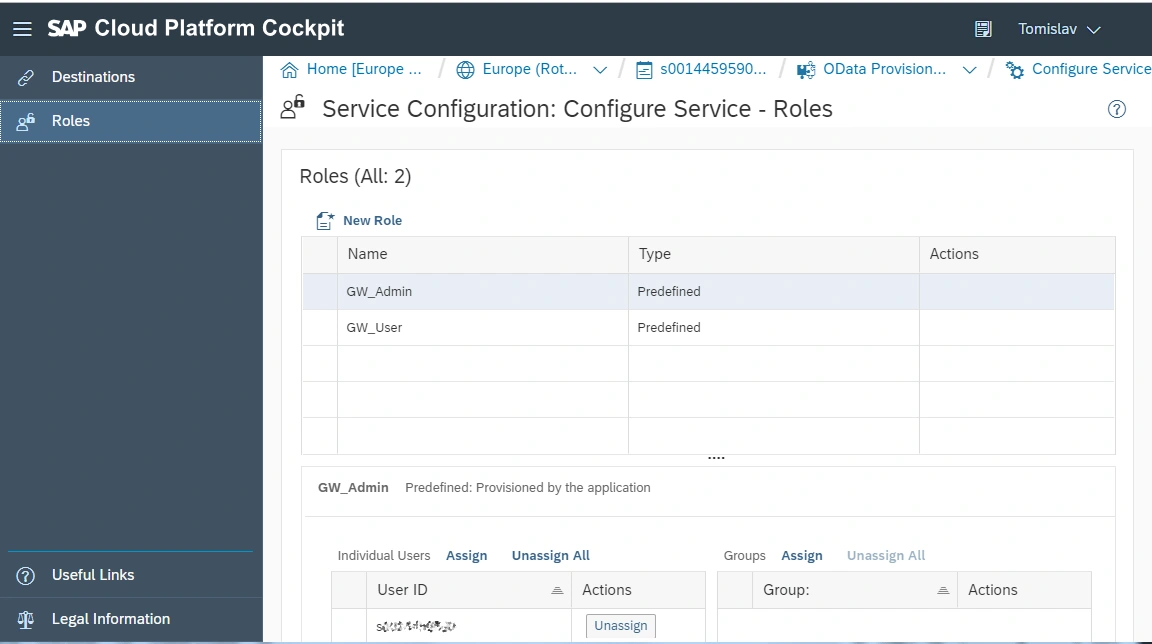
Next, we need to register our service in the OData Provisioning cloud service.
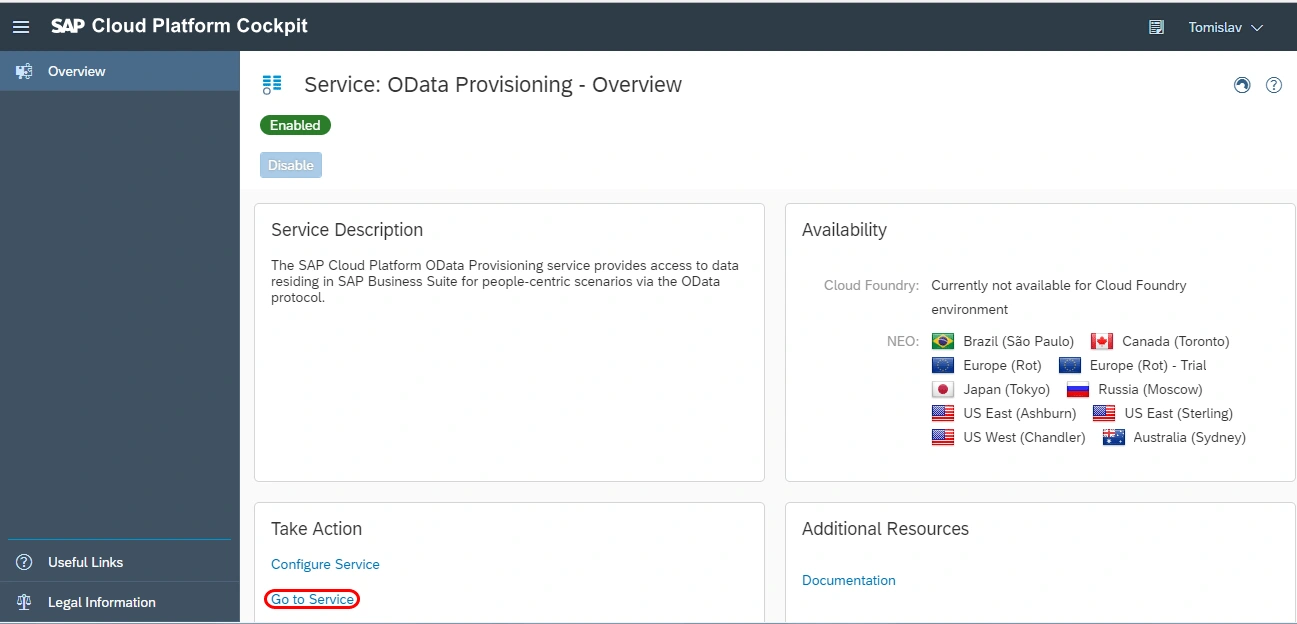
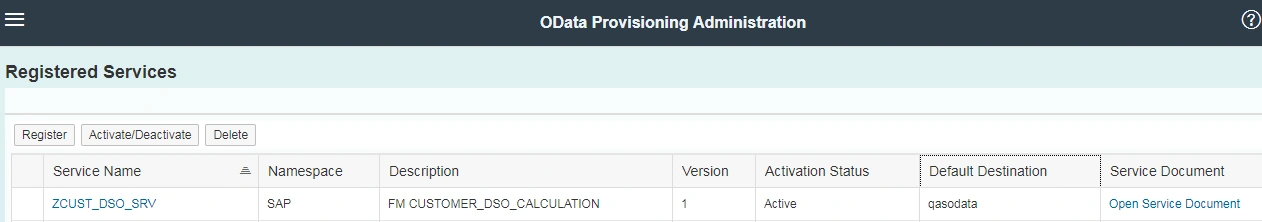
And the result is:
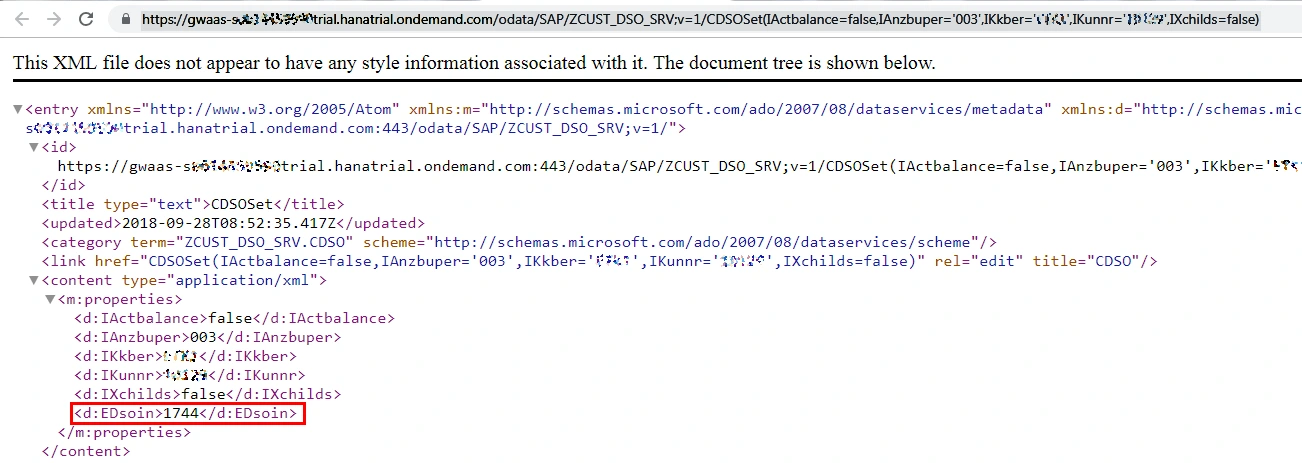
Embedded Service for CDS View for Purchase Orders
In the Eclipse IDE switch to the ABAP perspective by clicking the Open Perspective button or using the menu: Window -> Open Perspective -> Other.
Open the File menu, select New and then click on ABAP Project. Choose the ABAP backend system from the list of SAP System connections and press the Next button.
After ABAP Project has been created, choose your ABAP package ($TMP if you don't need a transport request) and from the context menu of your package choose New and then choose Other ABAP Repository Object.
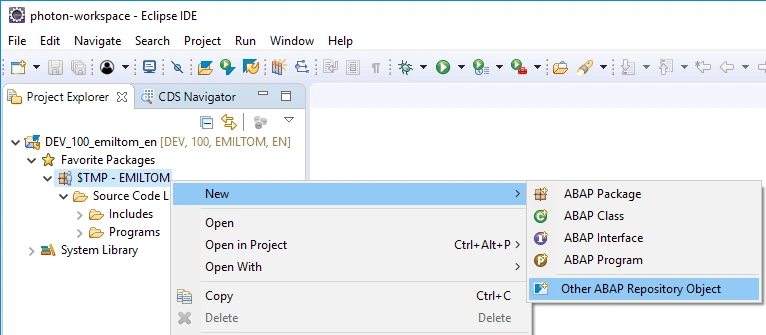
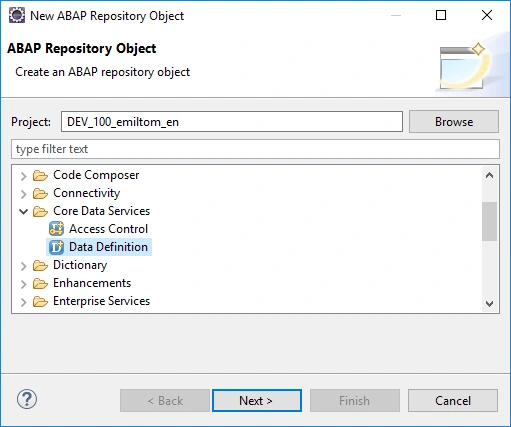
We create CDS view based on the chosen view template. Don't forget @Odata.publish:true annotation for automatically generating OData model definition, as well as the OData service runtime.
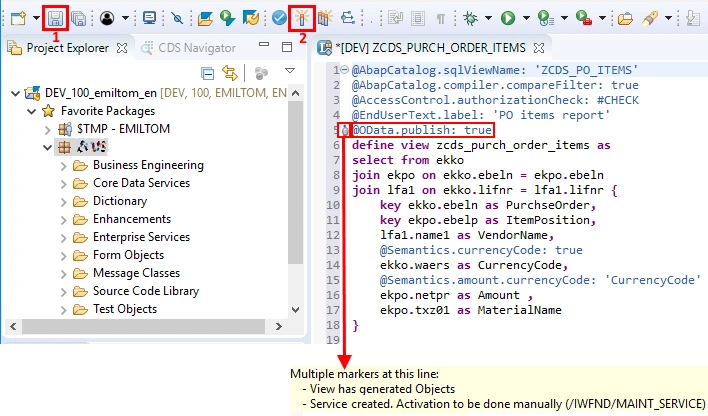
We can see the new decorator against the annotation which says that we need to activate the generated service in transaction /n/IWFND/MAINT_SERVICE.
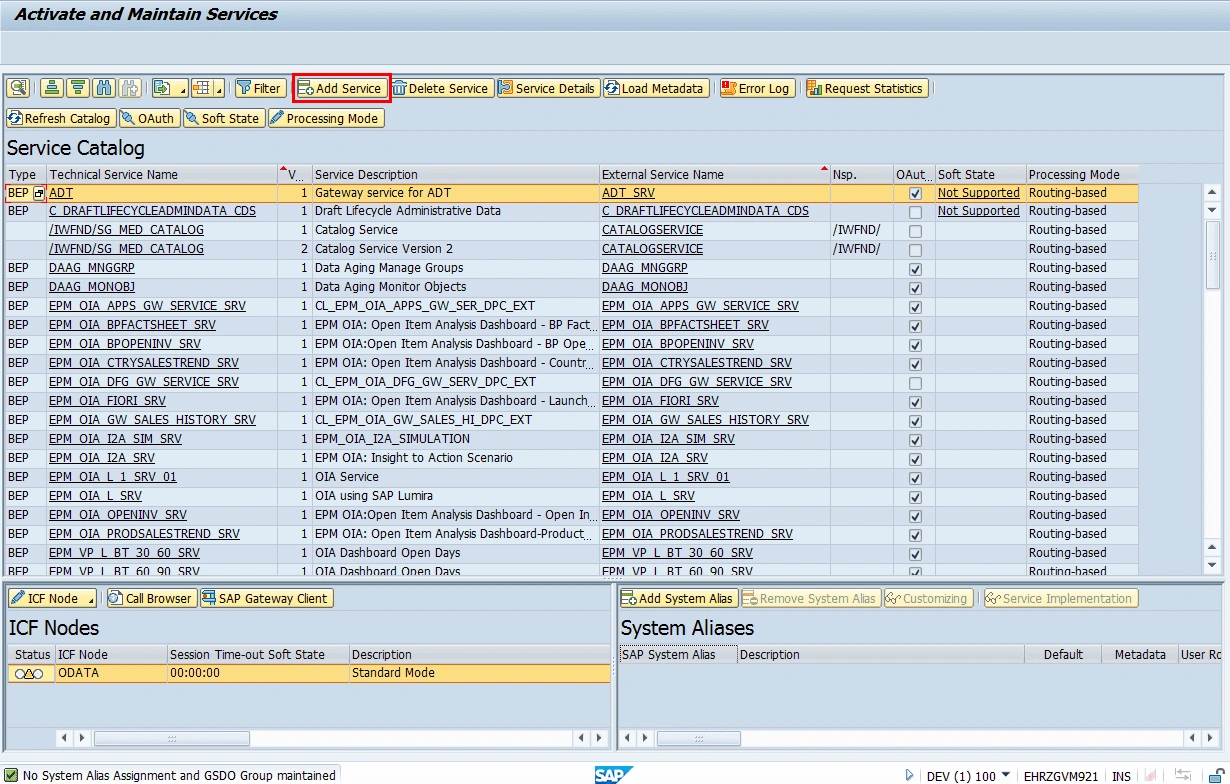
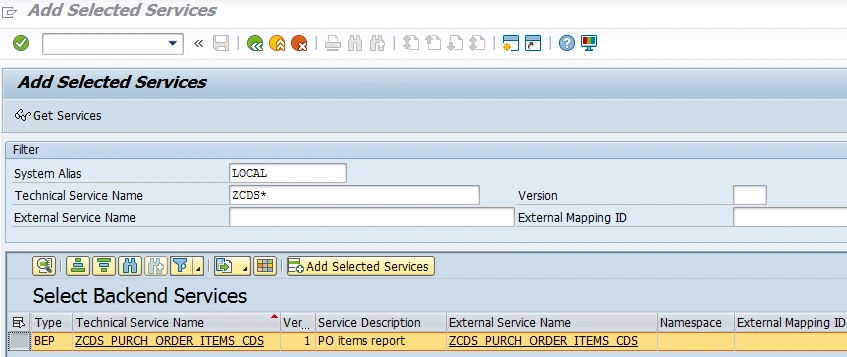
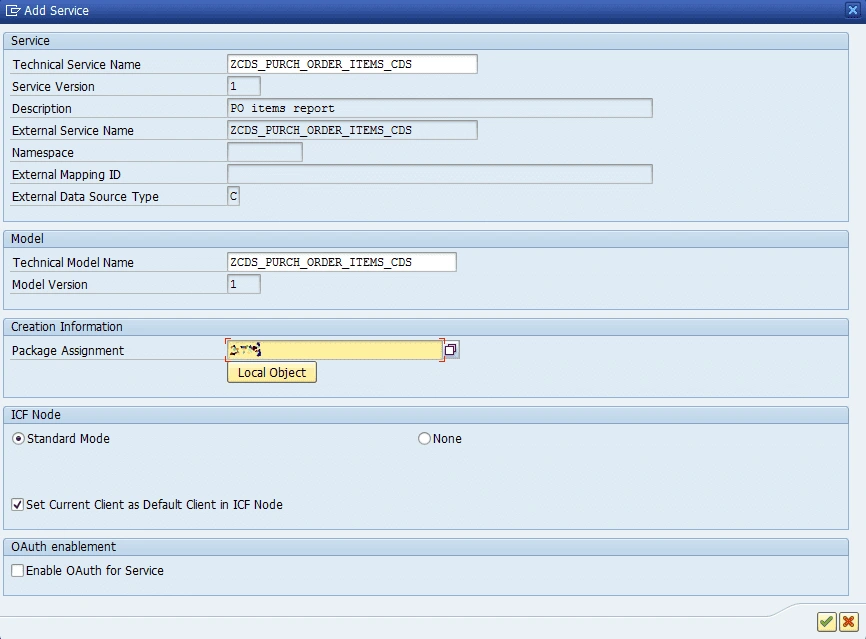
In the end, while calling OData service, I got an error notification because of the empty User Name field in the service's assigned system alias entry. I repaired that in the same way I described in the first service example.
Now we can call our OData service:
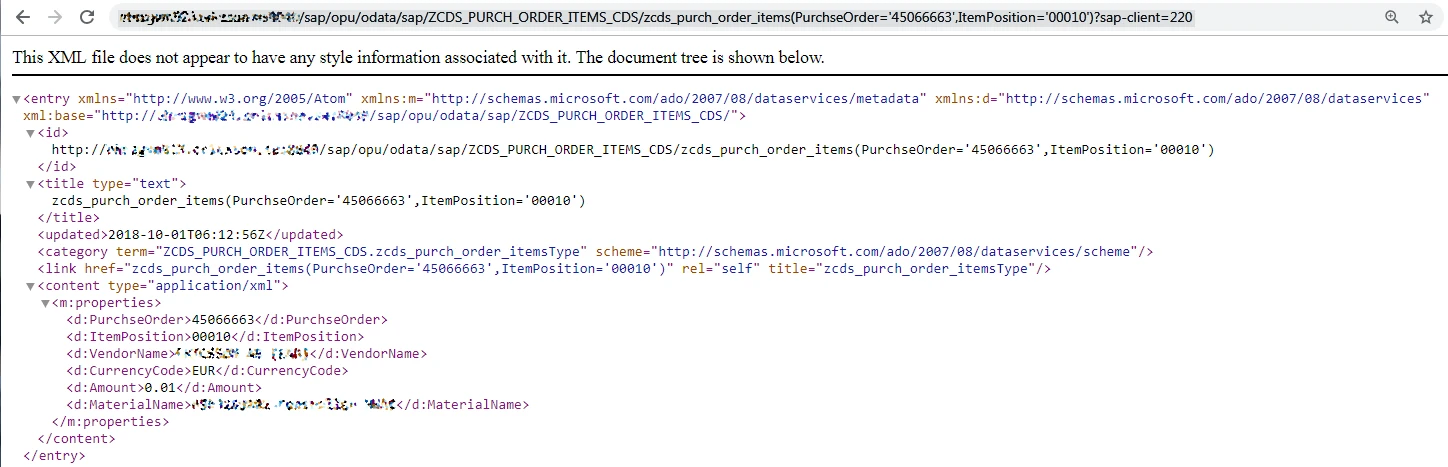
If we want to use OData Provisioning service, we need to register service as described in the previous service creation tutorial.
After service registration, we can generate Web IDE application based on our service. For that purpose, we need to create a destination which connects the Web IDE with the OData provisioning. It enables both tools to talk to each other.
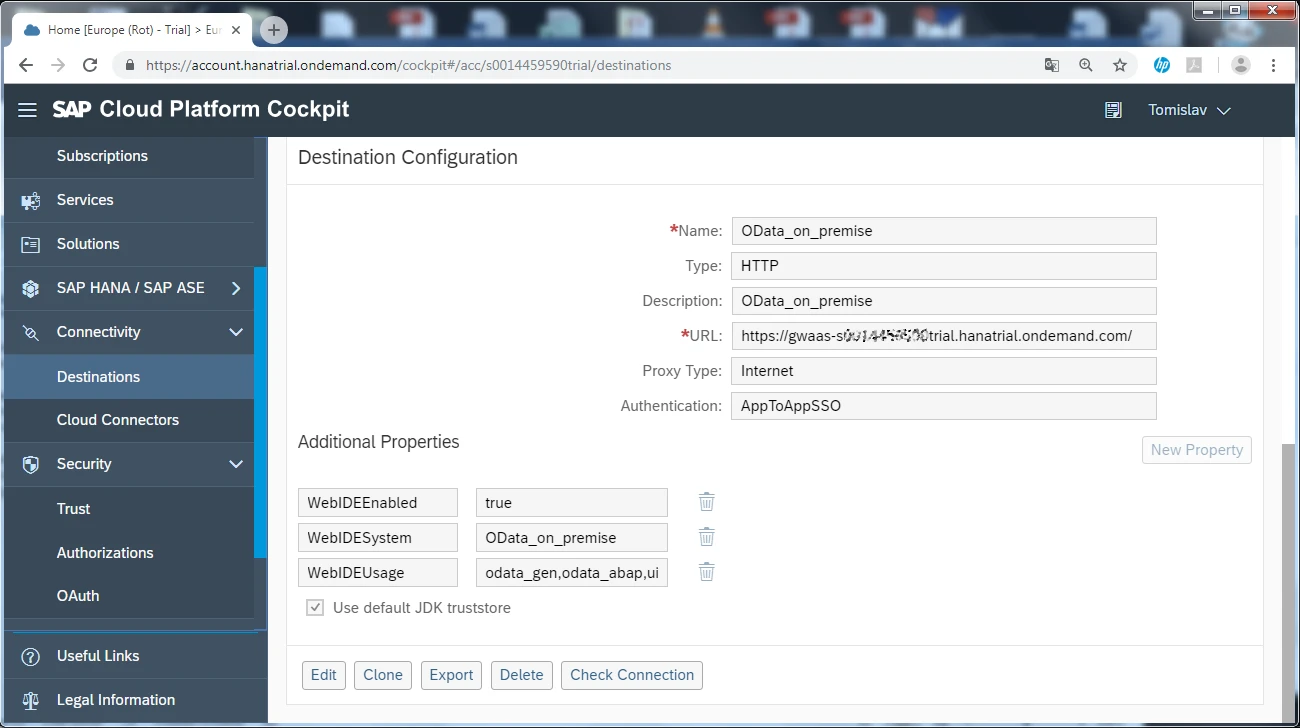
Now we are ready to generate Web IDE application based on our service. The word “generate” in the previous sentence implies that no development is needed.
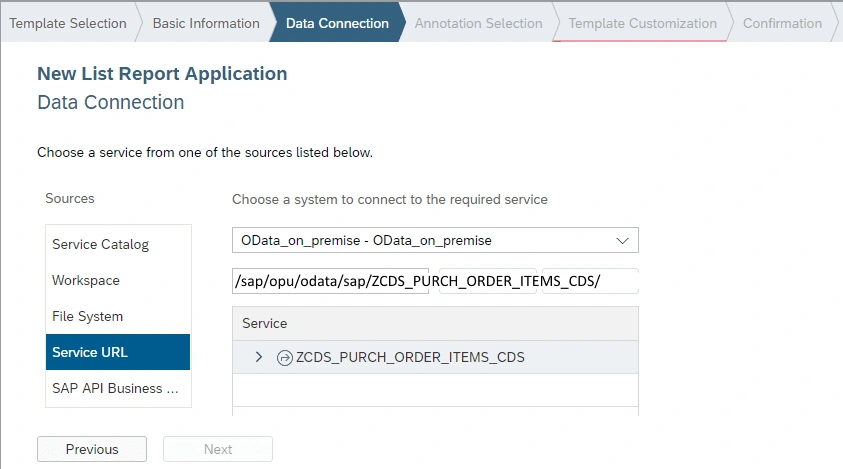
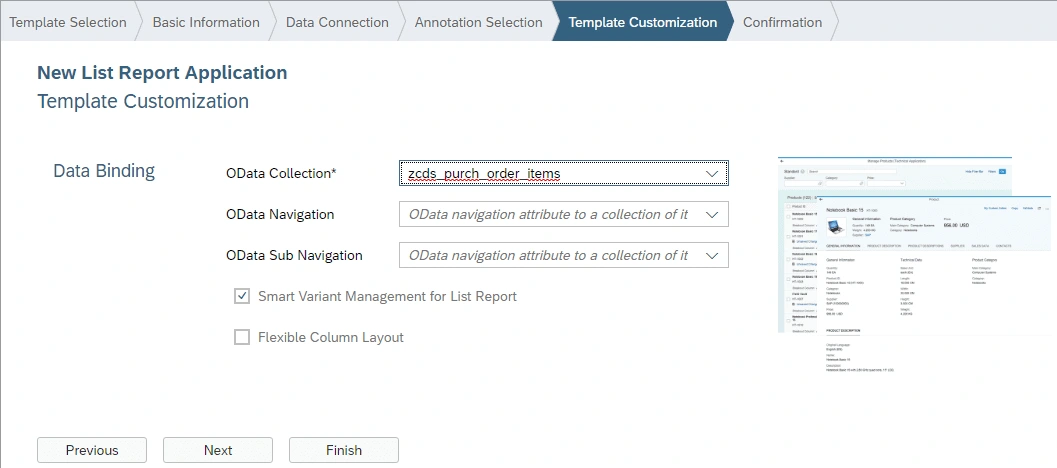
We choose File -> New -> Project from Template -> choose List Report Application and in the next step enter Project Name and Title. After that, you need to fill in your OData service details.
Now, we must create our SAP Fiori launchpad with our application in it.
The Fiori launchpad is fully integrated into Cloud Portal, and when you enable the Cloud Portal, the Fiori launchpad is also available with no additional manual steps.
The Administrator role for Cloud Portal is now defined as TENANT_ADMIN in HANA Cloud Platform; it is applicable for both Cloud Portal and Fiori launchpad. Click on Portal service, then click Configure Portal action choose Roles to add your user in TENANT_ADMIN role.
Go back to Portal service and click Go to Service. After that, click on Site Directory and choose Create Site.
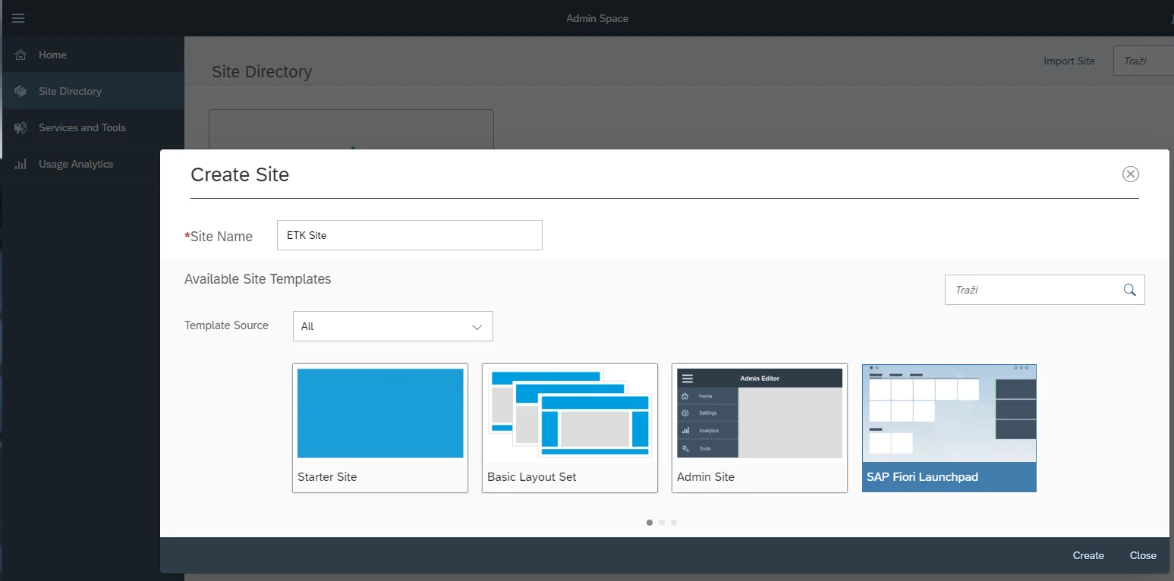
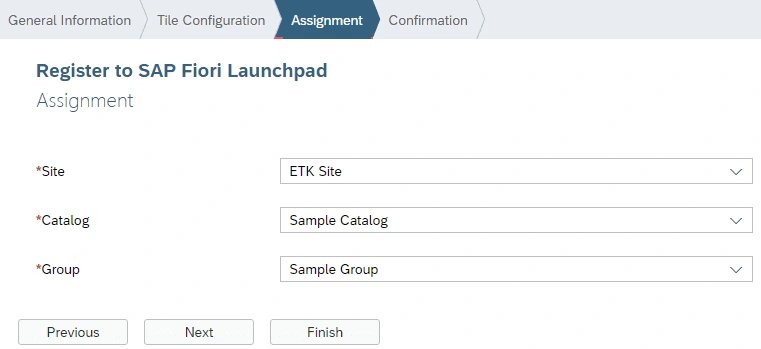
Now we are ready to deploy our application and register it to SAP Fiori Launchpad.
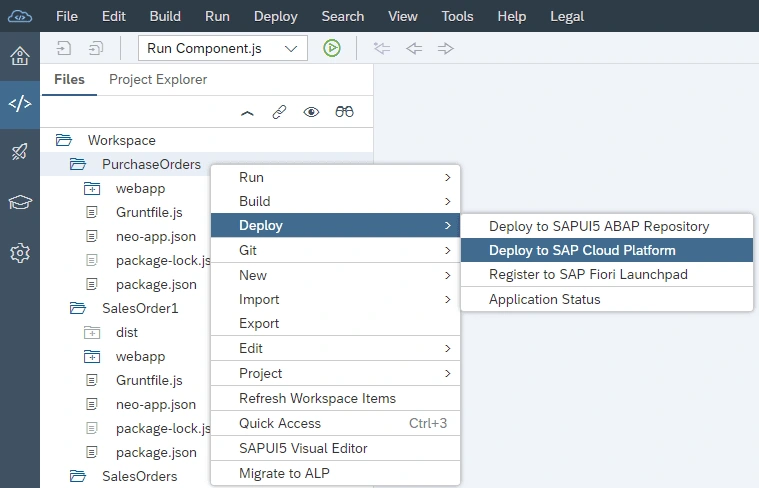
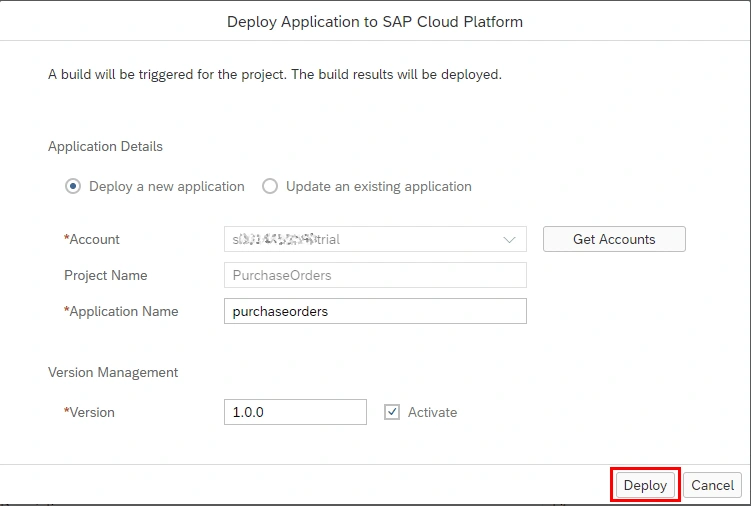
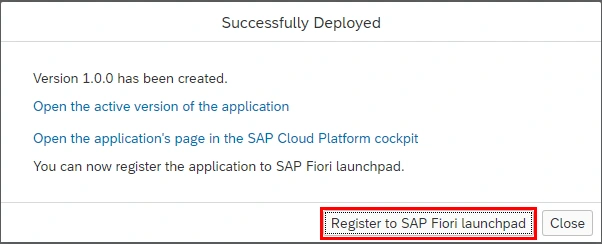
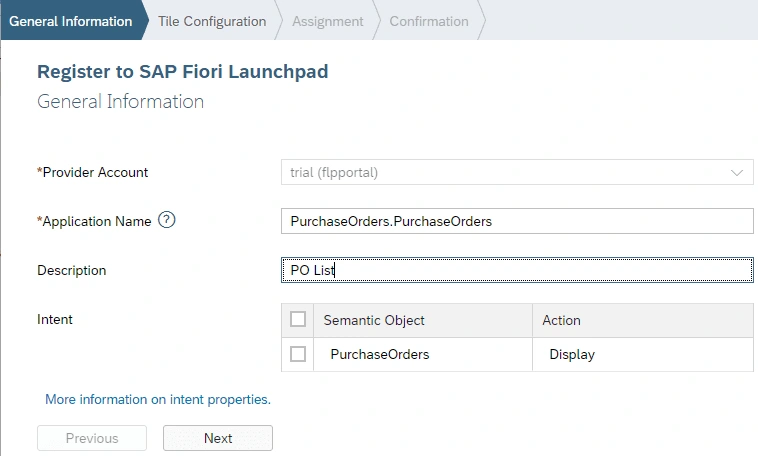
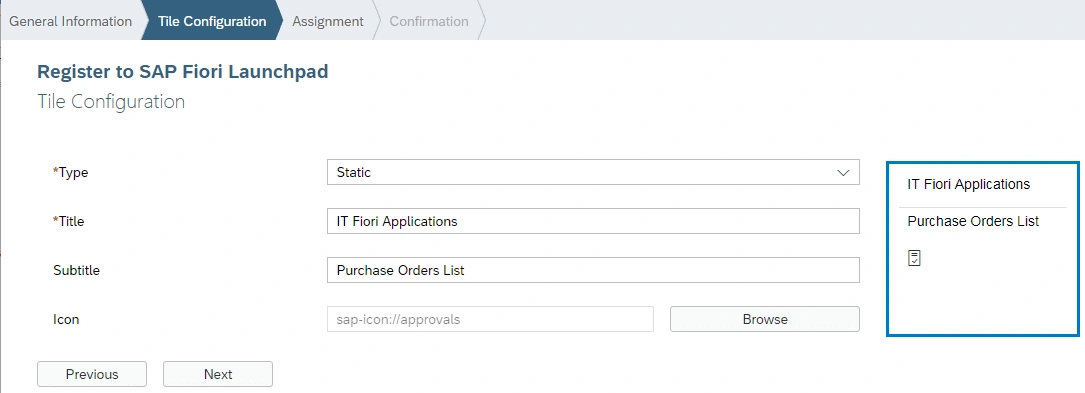

Click on Open SAP Fiori launchpad.
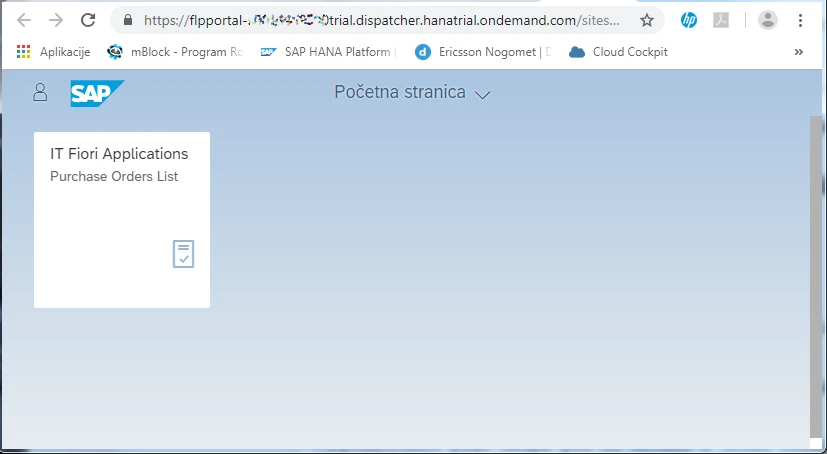
Click the application, then click the settings button 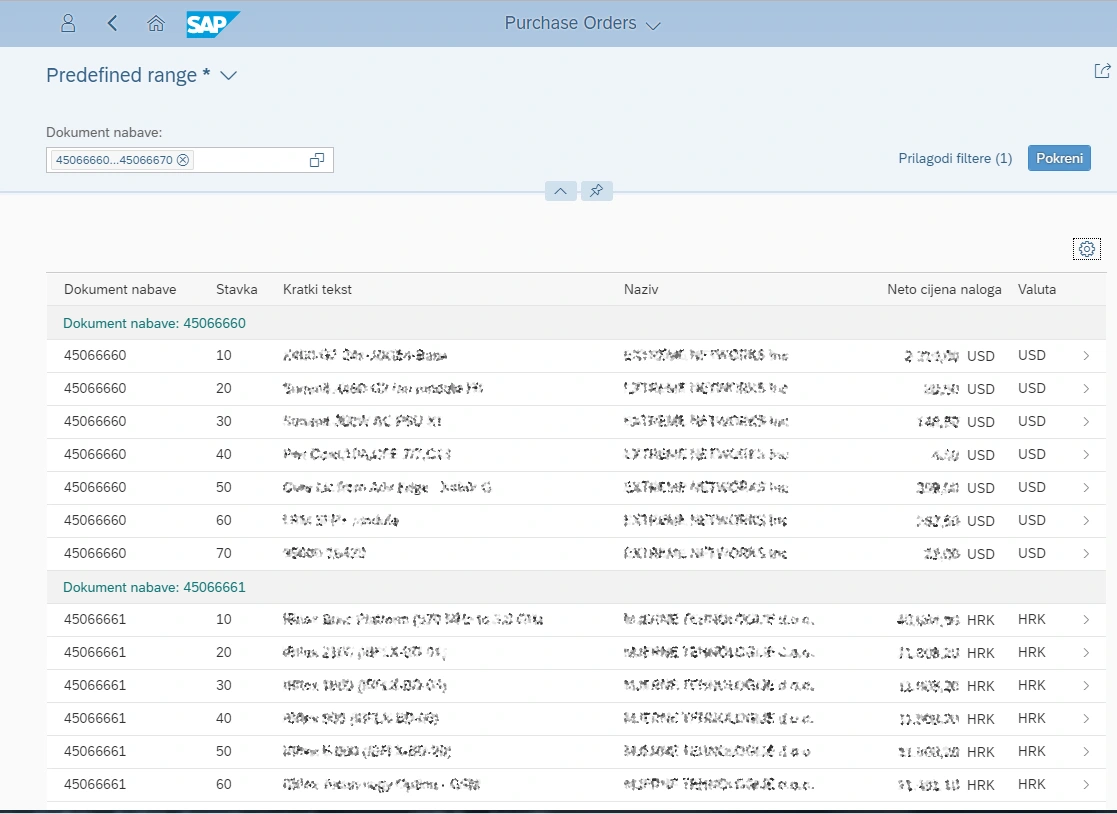 and check all columns. Then arrange filtering, sorting and grouping by your needs. We can see the purchase order items from our on-premise SAP system.
and check all columns. Then arrange filtering, sorting and grouping by your needs. We can see the purchase order items from our on-premise SAP system.
I hope you have enjoyed this quick look into OData Services for SAP Business Suite. Stay tuned to Eursap's SAP Blog, where we will be looking into things further in the coming weeks.
Author: Tomislav Milinovic