7 Next-Generation, HANA-Powered, Cloud-Based SAP Applications
7 Next-Generation, HANA-Powered, Cloud-Based SAP Applications.
Introduction
Since the launch of its new in-memory HANA database, SAP has continued on an ambitious and aggressive journey to introduce several next-generation, HANA-powered, cloud-based and on-premise SAP applications. While these SAP applications have created tremendous opportunities for companies to embark on a digital transformation journey, an overview of each of them will enable companies to make informed business decisions as to whether implementing them will bring enough business value and a return on their SAP investment.

Equally important, is that implementation of these latest HANA-powered SAP applications will create more career opportunities for SAP consultants in the future as they look to transition and upskill their current SAP experience to these newer SAP applications.
Before we begin with an overview, it is very important to emphasize that since S/4HANA will remain the digital core and the central ERP system on which the entire company will run its business, these next-generation, HANA-powered SAP applications will still need to integrate with S/4HANA in one way or another to ensure seamless and end-to-end business processes.
So let’s begin with an overview of S/4HANA.
1. S/4HANA
SAP S/4HANA Enterprise Management (S/4HANA, for short) is the successor of SAP ERP Central Components (ECC) – the de facto ERP system implemented by most companies over the last several decades. S/4HANA not only offers mostly all the components that were previously available in ECC but even more components, functionality, tools and features that were either unavailable in ECC or were part of other SAP standalone systems, such as SAP Customer Relationship Management (CRM) or SAP Advanced Planning and Optimization (APO).
While ERP components, such as, Materials Management (MM), Sales and Distribution (SD), Plant Maintenance (PM) are still very much there in S/4HANA including the newer ones, their categorization in S/4HANA is now inclined more towards different lines of business (LoBs) or are business processes-based, such as, order-to-cash, hire-to-retire, plan-to-product, sourcing and procurement, and procure-to-pay amongst others.
If you are an ECC consultant and intend to upskill or reskill yourself in S/4HANA, then check Eursap’s blog How to successfully transition your SAP career from ECC to S/4HANA.
2. C/4HANA
SAP C/4HANA is an end-to-end customer relationship management (CRM) application. Implementing C/4HANA helps in ensuring smoother sales and customer service processes. SAP C/4HANA has five components, each targeted to managing different aspects of customer engagement. The five C/4HANA components are:
SAP Commerce Cloud
This C/4HANA component gives companies the ability to create products and services catalogues from which customers can choose and order.
SAP Sales Cloud
This C/4HANA component is an end-to end solution to support and facilitate sales teams throughout the selling cycle. It also gives customers an easy way to find information relating to a company's products or services. In addition, it captures additional information about the customers for the sales teams to upsell or create new products or services. It tracks all stages of sales order management from a product's or service's ordering to its delivery. It ensures timely and error-free billing for the delivered products or services.
SAP Marketing Cloud
This C/4HANA component enables companies to integrate their various marketing initiatives, such as advertisements in print, electronic or social media, and through analytics gives them the ability to track which marketing efforts are converting into sales.
SAP Service Cloud
This C/4HANA component enables companies to better attend customers who request a return, replacement or refund for the delivered products or services with a hassle-free experience. It also completely supports multi-channel customer engagement.
SAP Customer Data Cloud
This C/4HANA gathers data of known and unknown visitors to a company’s website. This data is then evaluated to ensure more proactive engagements with visitors as well as gaining insights on the kinds of products and services visitors are interested in, inquire about or search for.
Companies using SAP S/4HANA or even SAP ECC Sales and Distribution (SD) can integrate them with SAP C/4HANA to bring greater efficiency to the entire sales process. Similarly, SAP SD or SAP CRM (Customer Relationship Management) consultants can consider reskilling or upskilling themselves in SAP C/4HANA.
3. SAP Ariba
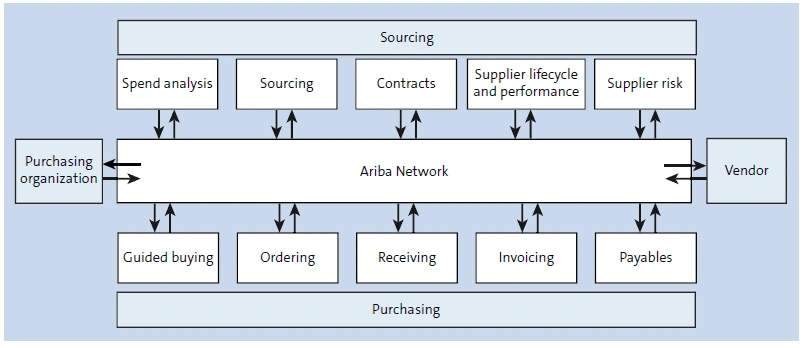
SAP Ariba Network in a holistic e-commerce platform that connects buyers and suppliers from all over the world. It facilitates collaboration amongst various stakeholders and also enables self-service by ensuring seamless communication of procurement processes. It enables companies to source suppliers globally and at the same time suppliers can also register themselves with companies – hence SAP Ariba Network is a complete and integrated marketplace. SAP Ariba Network is a good fit for companies that want their suppliers to directly interact with their systems. But if the company’s procurement process is mostly managed in-house, and remain within the SAP system’s firewall, then S/4HANA Materials Management (MM) may suffice.
Figure 2 shows an end-to-end procurement process and how the communication between a vendor takes place with a company’s purchasing organization using SAP Ariba Network.
Companies using SAP S/4HANA or even SAP ECC Materials Management (MM) can integrate them with SAP Ariba Network to bring greater efficiency to the entire procurement process. Similarly, SAP MM or SAP SRM (Supplier Relationship Management) consultants can consider reskilling or upskilling themselves in SAP Ariba Network.
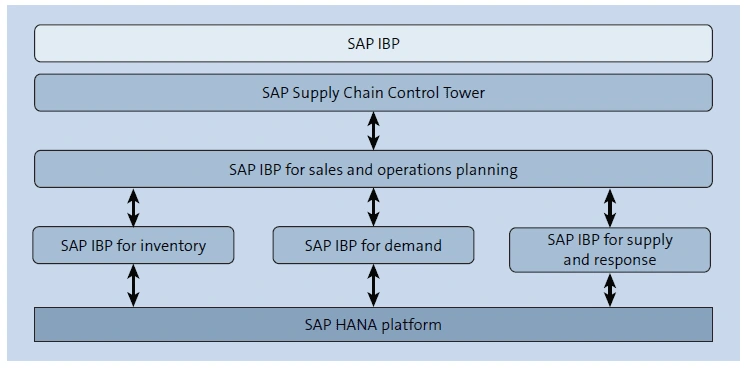
4. SAP Integrated Business Planning (IBP)
SAP IBP for sales and operations.
This IBP component balances a demand plan by agreeing to a supply plan to ensure maximum utilization of a company’s resources and assets.
SAP IBP for demand
This IBP component brings together the traditional forecasting techniques with greater accuracy in demand sensing – all the while taking advantage of machine learning and demand sensing tools available.
SAP IBP for inventory
This IBP component optimizes the inventory levels so as to maintain sufficient inventory coverage across the entire supply chain.
SAP IBP for response and supply
This IBP component manages the long-term forecast’s figures with shorter-term demand and supply situations by refining replenishment orders such as procurement or production orders to meet the supply requirements. It also prioritizes the entire sales process by aligning demand that meets customers’ needs whilst ensuring it also adheres to the company’s business priorities.
SAP Supply Chain Control Tower
This IBP component provides end-to-end visibility throughout the supply chain by integrating data from SAP and non-SAP systems with ad-hoc analysis and alerts. It provides insights into the supply chain’s key performance indicators (KPIs) in the form of intuitive dashboards.
Companies using SAP S/4HANA or even SAP ECC Production Planning (PP) can integrate them with SAP IBP to optimize their supply chain management. Similarly, SAP PP or APO consultants can consider reskilling or upskilling themselves in SAP IBP.
5. SAP SuccessFactors
SAP SuccessFactors HCM Suite provides an end-to-end solution of hire-to-retire business process. The hire-to-retire process begins with the decision to begin the hiring process to fill in a position to final selection, on-boarding and subsequently all human resource-focused activities, including learning & development and performance evaluation, during the entire stay of an employee in an organization.
The key HCM processes within SAP SuccessFactors HCM Suite are as follows:
Core HR and payroll
In the process, maintaining complete and comprehensive information of an employee is ensured, including bank account details, address and phone numbers, so that subsequently HR-related business functions can run smoothly.
SAP SuccessFactors Employee Central component tracks all HR information pertaining to an individual including time off and leave. It supports the managers in effectively managing their team members’ activities such as changing an employee’s role, recommending revised compensation to reflect performance or even suggesting letting go an employee on the basis of unsatisfactory performance, disciplinary or compliance issues. The payroll process is also managed in this component that eventually leads to employees getting paid.
Time and Attendance Management
Given that paying employees is directly linked to attendance, time management and expenses management, it is crucial to capture this important information completely and correctly. Employees working remotely or on business travel can still record all relevant information.
Recruiting and Onboarding
In the hire-to-retire business process, the importance of ensuring to recruit and hire the best talent cannot be overemphasized - including identifying, engaging and onboarding new recruits. Two solutions cover these business processes: SAP SuccessFactors Recruiting and SAP SuccessFactors Onboarding.
Learning and Development
For retaining top talent, it’s imperative for companies to offer career development and on-going learning opportunities for employees. When there’s an internal reorganization, such as promotions or job roles change, then these two need to facilitate employees by making tools and resources available to effectively perform their new roles. Learning and development business processes is provided by SAP SuccessFactors Learning and SAP SuccessFactors Succession & Development.
Performance and Compensation
Compensation for employees may directly or indirectly be linked to performance. For example, it is common for a sales team to be given sales targets. Meeting or exceeding these sales targets may lead to performance bonuses. Similarly, it’s important to define measurable, attainable, realistic, and timely (SMART) goals for employees that can then be compared to see if they were achieved or otherwise and to form the basis of a performance evaluation. Two solutions meeting these business processes are SAP SuccessFactors Performance & Goals and SAP SuccessFactors Compensation.
Workforce Planning and Analytics
Workforce planning helps organizations ensure that they have the right people with the right skillsets - both from an immediate as well as strategic perspective. Workflow analytics ensure that data pertaining to an organization’s workforce is accessible to help companies make informed business decisions. Both capabilities are available in SAP SuccessFactors Workforce Planning and SAP SuccessFactors Workforce Analytics solutions.
Companies using the S/4HANA or even SAP ECC Human Capital Management (HCM) can integrate them with SAP SuccessFactors to bring greater efficiency to the entire hire-to-retire process. Similarly, SAP HCM consultants can consider reskilling or upskilling themselves in SAP SuccessFactors.
6. SAP Concur
SAP Concur is a travel and expense management application that companies can use to effectively manage employees’ travel planning, expenses incurred during travelling as well as reimbursement of travel-related expenses. SAP Concur is available in three options:
Standard:
This option is suitable for small-to-mid sized companies that require limited travel and expense management functionality. This option is available in selected countries and regions only.
Professional:
This option offers far greater choices on the functional, as well as the technical, sides of travel and expense management and is more suited for mid-to-larger-size companies.
Premium:
This option offers even greater flexibility to customize solutions to meet complex travel and expense management requirements of larger companies having global footprints and operations.
7. SAP Fieldglass
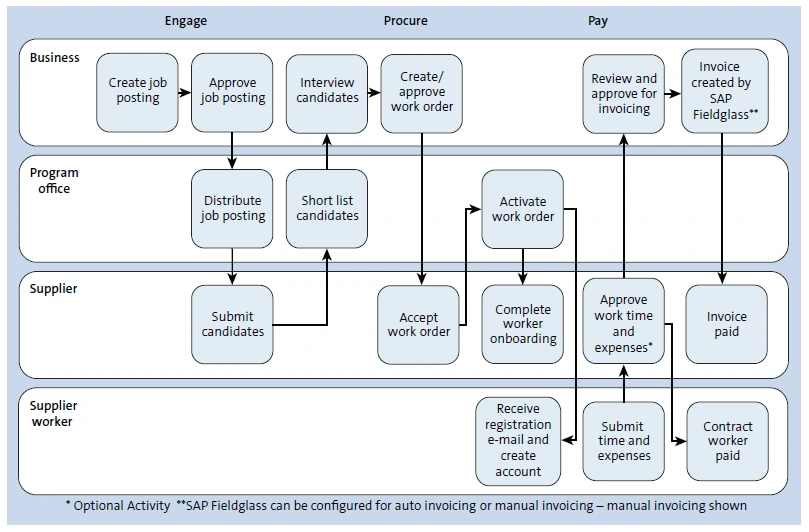
SAP Fieldglass is an external and contingent workforce and services management application that connects a company’s need for temporary, specialized experts with freelancers, industry experts or companies providing specialized or general manpower. In order to cater to different and diverse needs of workforce or services management professionals, SAP Fieldglass is available in two offerings – simple and a complex contingent workforce management.
Figure 6 shows an end-to-end process of a simple contingent workforce management solution which starts when the company advertises the position to be filled. The workforce supplier submits relevant candidates’ profiles to the company and the company shortlist. This is then followed by the company undertaking its internal procurement process such as creating a work or a purchase order for the contingent workforce supplier followed by onboarding the selected candidate. The payment process begins when the contingent workforce supplier submits the invoice to the company including supporting documents such as timesheets and actual expenses incurred.
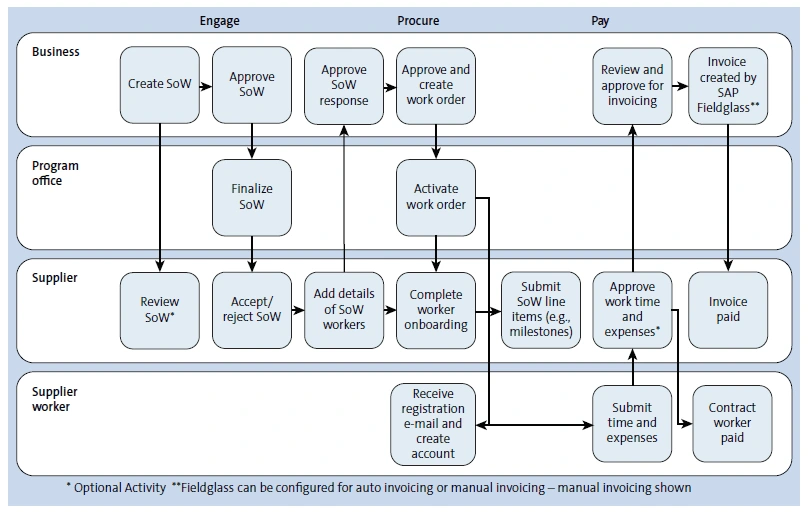
If a company has requirements of a large and a complex mix of contingent workforces, then the company and the contingent workforce supplier work together to create a State of Work (SoW). A SoW aligns expectations and deliverables of both parties and is used for tracking and monitoring compliance which ensures timely payments to contingent workforce suppliers. Figure 7 covers an end-to-end business process.
Where to find further resources on next-generation, HANA-powered, cloud SAP applications
Below is a summary of some of the resources available:
1. SAP PRESS book: SAP: An Introduction - Next-Generation Business Processes and Solutions
2. Several SAP PRESS books on each of next-generation SAP applications
3. Free OpenSAP courses
4. If you work with an SAP Partner, then SAP Partner Edge offers several valuable resources
Author: Jawad Akhtar – Author of four SAP PRESS books.