Currency Translation - The Backbone of SAP Group Reporting
SAP Group Reporting: Currency Translation - Backbone of SAP Group Reporting.
Abstract
Corporate groups must prepare their consolidated financial statements using the group currency. If the local currency of the consolidation unit is different from the group currency, need to translate the local currency into the group currency. The translation rules are defined in each CT methods, which is assigned to individual consolidation units. If the local currency of the consolidation unit is the same as the group currency, the system always copies the value in the local currency to group currency.
Introduction
In today’s global business environment, multinational corporations operate across multiple geographies, each with their own functional currency. For effective consolidation, SAP S/4HANA Finance for Group Reporting provides a robust framework for currency translation (CT). This process translates local currency (LC) values into the designated group currency (GC). (The group currency is the currency in which the consolidation group publishes its financial statement. It is defined in the consolidation version)
This functionality is critical because group-level financials must be comparable and reliable. SAP emphasizes that before executing the CT task, organizations must maintain exchange rates and assign appropriate translation methods to each consolidation unit. Once executed, the CT process ensures that local financial statements are accurately reflected in group currency, forming the basis for meaningful consolidation.

Currency Translation Methods in SAP Group Reporting
All entities send their trial balances to corporations at month-end. Currency translation converts local currency values into group currency values. Different exchange rates (average and Closing) will be applied to different types of accounts.
For example: --
• Profit and Loss items at average rate
• Balance sheet at closing Rate
• Currency translation adjustments: Post to original FS Items for non-historic items.
• Currency translation adjustments: Post to separate FS Items such as Currency Translation Adjustment (CTA) for historic and income related.
In summary, we divide FS Items into two types. P&L and Balance Sheet. Again, we can divide Balance Sheet FS Items into two types as Historic FS Items and Non-Historic FS Items.
Non-Historic FS Items means Monetary accounts such as cash, AR, AP, Inventory, Buildings, Fixed Assets etc.
Historic FS Items are non-monetary accounts. These FS Items will be treated using Historical cost. They should be translated using exchange rate at the date of Transaction (Original Rate) . Example: Share capital, Other Equity, Goodwill, Current Year Retained earnings, etc
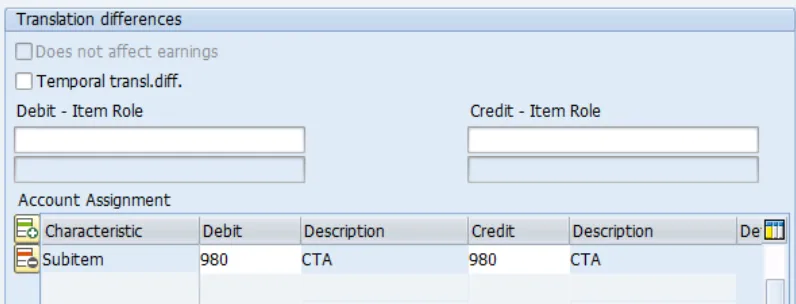
• For Non- Historic FS Items When system Translates from Local Currency to Group Currency, the differences will be posted to same FS Items. But it uses Subitem 980. (Currency translation adjustments: Post to original FS Items for non-historic items.)
Designing Historic & Income Currency Translation
Historic items include investment, equity, and goodwill FS items for example. Income related items include retained earnings and profit & loss fs items for example. CTA for historic and income related items is posted to CTA FS items with a unique CTA transaction type.
How does translation happen?
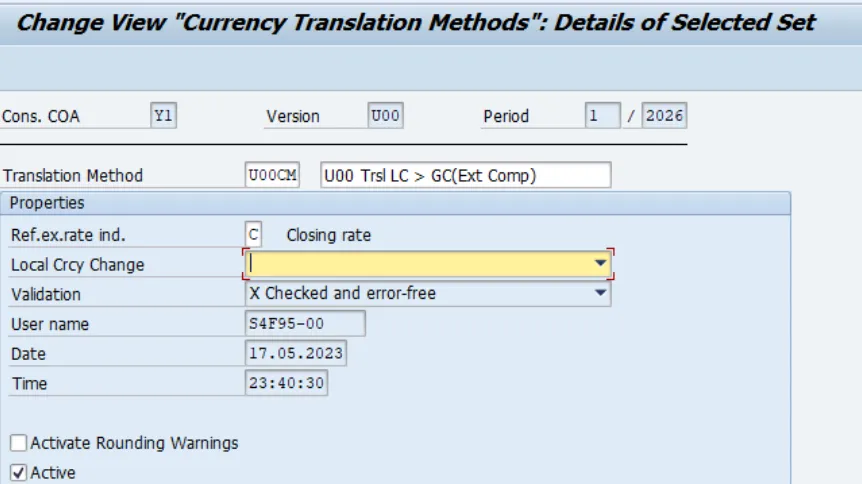
1. In the first currency translation (CT) step, reported financial data is translated from the local currency amount into the group currency using the reference exchange rate for all FS items. This first translation helps detect translation differences in a later step and ensures that the overall translation is balanced. The reference exchange rate always uses the Closing Rate exchange rate type. We give reference exchange rate indicator in below screen
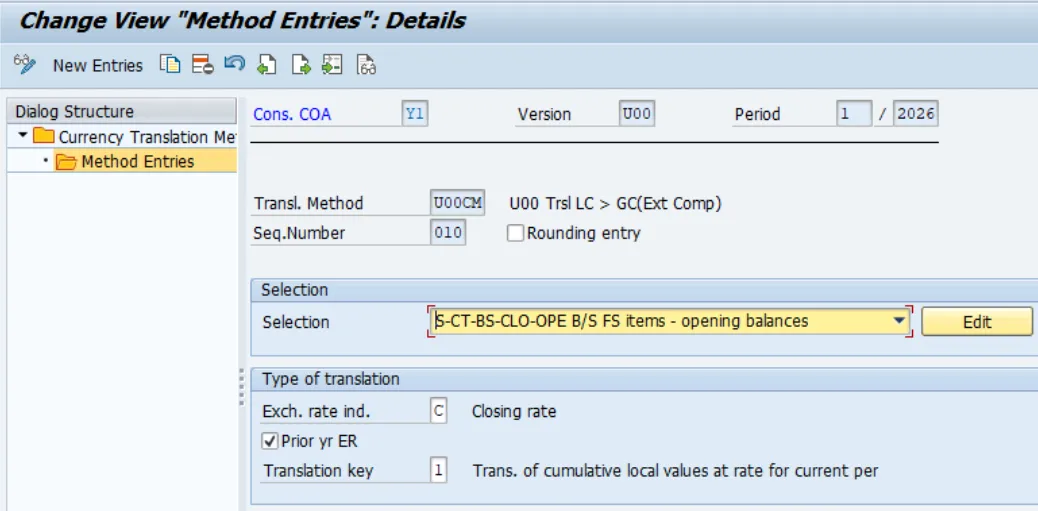
2. In the second step, the local currency amounts of the specified combinations of FS items and subitems are translated into the group currency by applying their respective exchange rate types, for example, the Average Rate. The CT method determines the exchange rate types used and the FS items to which the incurred translation and rounding differences are posted.
3. In the third step, the difference between reference translation (first step) and special translation (second step) is calculated and stored on a different accounting object, for example, on the same FS Item for a currency translation difference subitem or on a difference FS Item, such as the currency translation reserve.
IMPORTANT: When you run the task, the data posted in the previous run is not deleted but rather delta data is posted. In other words, a delta is calculated by aggregating the results from the previous run and the current run.
Configuration steps for Currency translation in group reporting in SAP S/4HANA
SAP S/4HANA for Group Reporting> Currency Translation for Consolidation> Maintain Exchange Rates
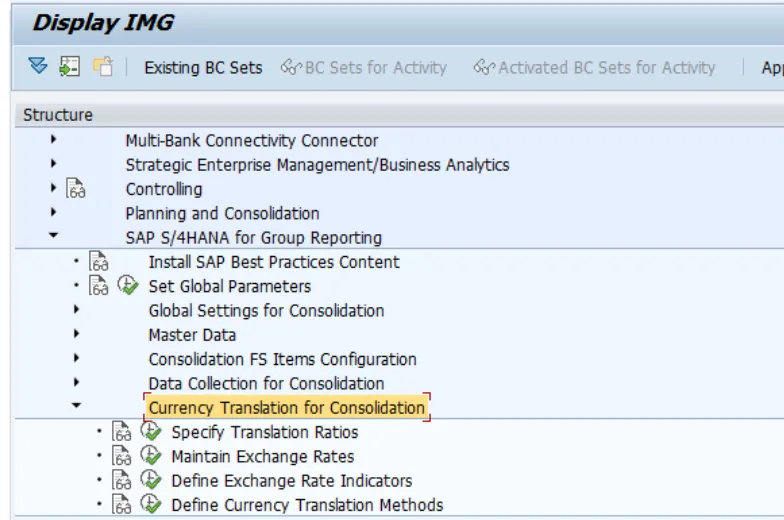
Or you can also Maintain Exchange Rates using below path
Fiori App: Manage Global Accounting Hierarchies → Currency Exchange Rates
Backend IMG Path: SPRO → SAP Reference IMG → Financial Accounting → Financial Accounting Global Settings → Currencies → Enter Exchange Rates
• Update rates for the relevant period:
o AVG (Average Rate): For P&L accounts.
o CLO (Closing Rate): For balance sheet accounts.
IMPORTANT: For actuals, update exchange rate type AVG and CLO, for planning scenarios, update exchange rate type AVG1 and CLO1, and for simulation of actuals, update exchange rate type AVG2 and CLO2.
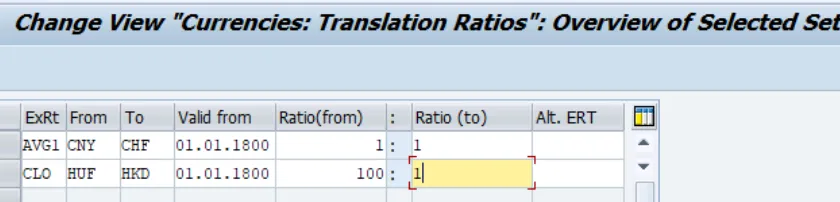
Specify Translation Ratios
Specify translation ratios for each combination of exchange rate type and source and target currency for translation.

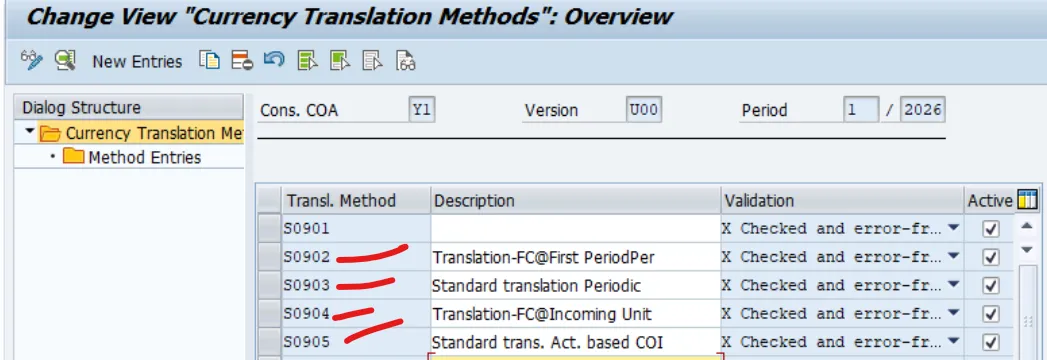
Define Currency Translation Methods
The currency translation (CT) methods define how the currency translation takes place depending on the financial statement (FS) items and subitems.
From the IMG, go to Currency Translation for Consolidation – Define Currency Translation Methods to create a currency translation method.
You can choose from the following pre-delivered currency translation method, based on your business needs
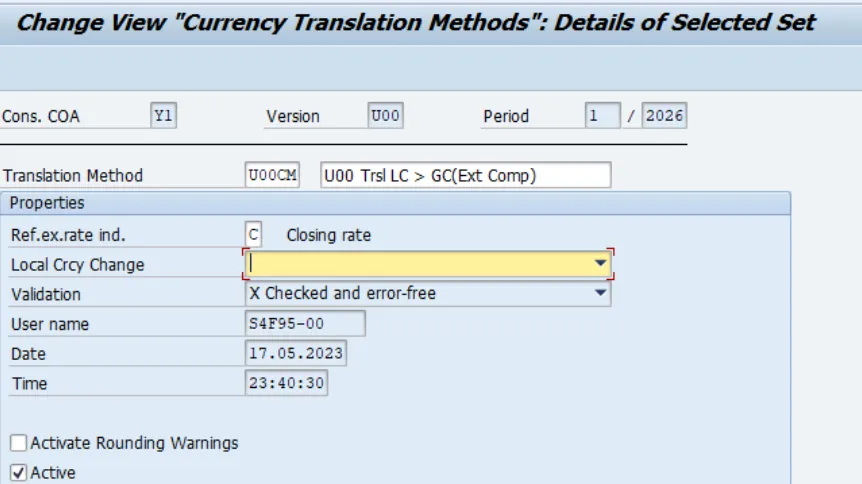
A currency translation method is used to specify the reference exchange rate (such as the closing rate). You can see in below screen
Below is an example currency translation method.
Here in this screen, we defined reference rate Indicator = C.
All sequences in this CT Method will use the closing rate as the reference rate.
Then sequence entries are to be defined . Methods consist of sequences. Each sequence is used to translate sets of FS Items and transaction types such as non-historical balance sheet movements at average.
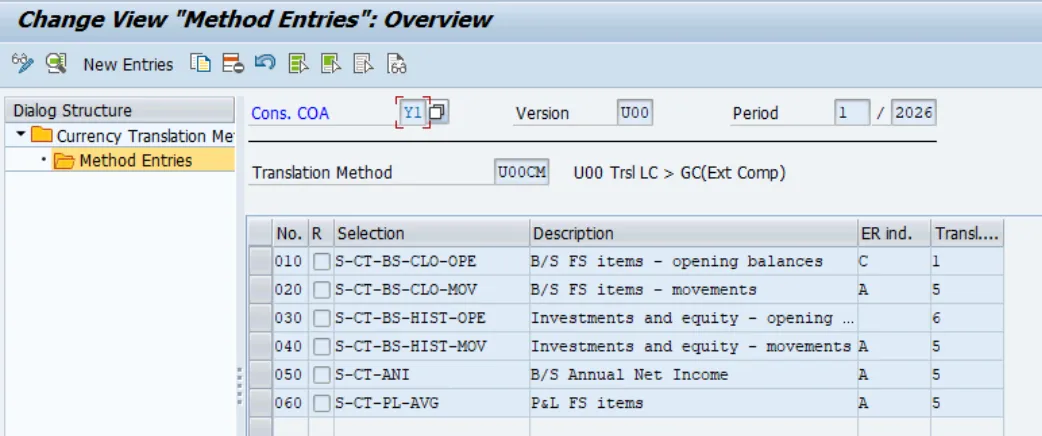
From the above screen I have taken an example of sequence 010 ( Currency Translation - Opening Balance Sequence 010). This sequence is to translate Non Historical Opening Balance of Balance sheet FS Items at the Prior year exchange rate. We use closing Rate- that means Prior year end Rate.
Translate the Year to date values at Period rate. As adjustments posts to same FS Items, I have kept Debit and Credit FS Item blank. These will show using Transaction Type 980. You can see those details in below screenshot.
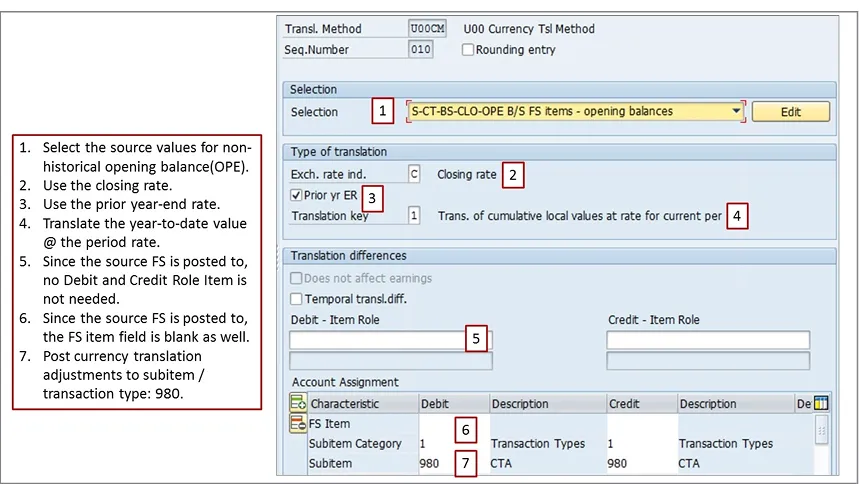
*Since the opening balance is stored on period 000, the amount in the group currency is kept at its original value.
Similarly sequence 020 - Currency Translation - Movement Sequence 020
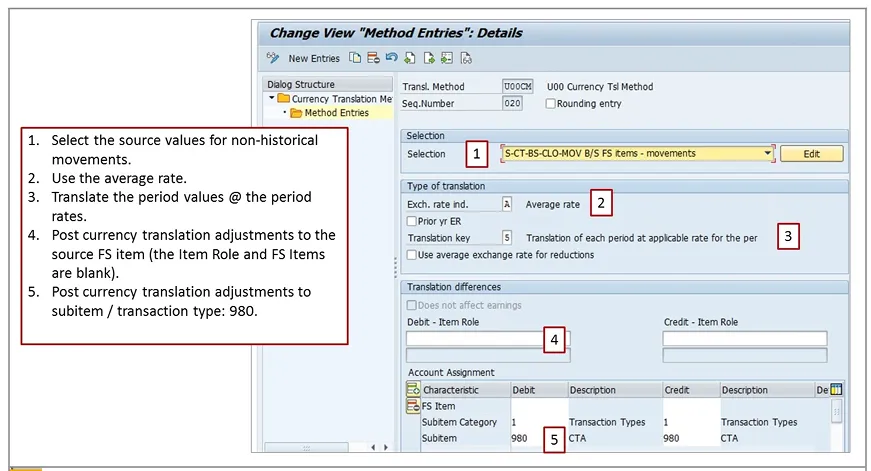
Sequence 020: This sequence translates the movements using the average rate for each period
Exchange Rate: Avg Rate for non-historical movements. Adjustments posts to the same FS Item. Transaction Type 980.
How Historic FS Items Translation Happens?
Historic FS items include investment, equity, and goodwill fs items. Income related items include current year’s retained earnings and profit & loss fs items.
CTA for historic and income related items is posted to CTA fs items with a unique CTA transaction type. If there are already source system group currency values, they can be used by SAP S/4HANA Finance for group reporting without any re-translation.
How to configure Currency Translation - Historic Opening Balances
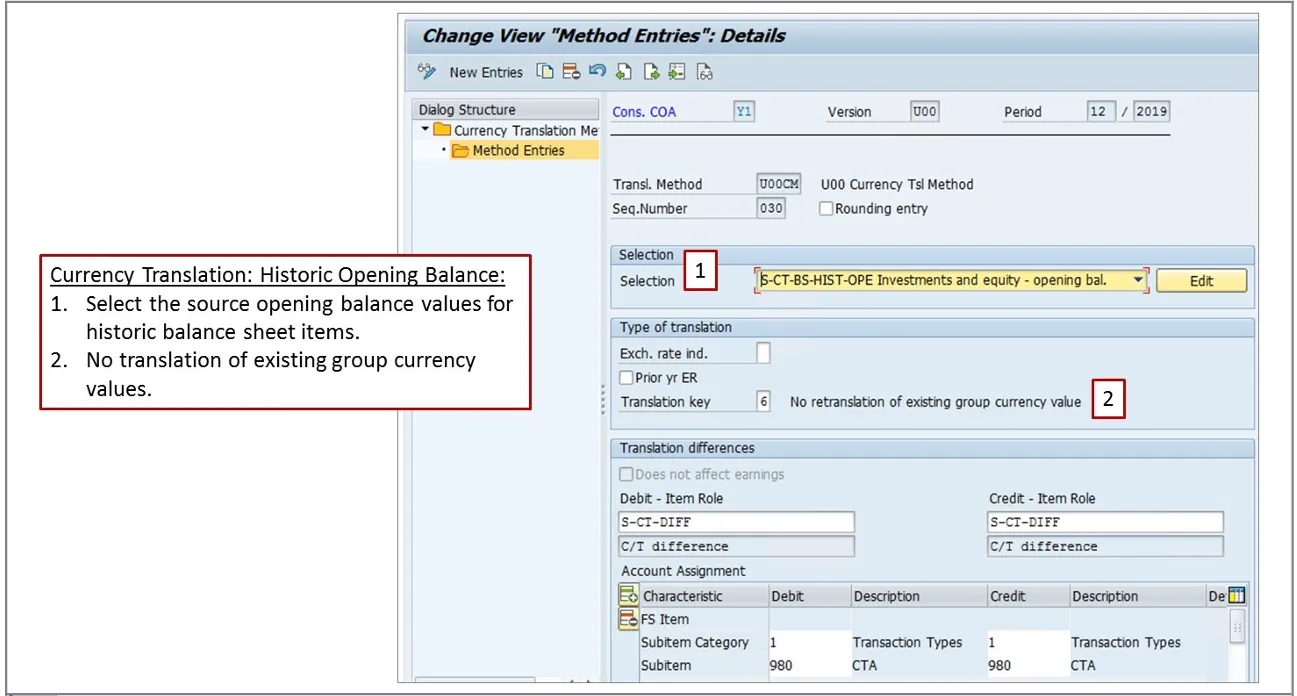
In the above screen Print, the sequence to translate historical opening balances is configured:
• Select the source values for historical opening balances
• The exchange rate indicator is blank when translation key 6 is used
• No re-translation of existing group currency values
• Post translation differences to the FS item 314800 (determined via FS item role S-CT-DIFF)
• Post currency translation adjustments to subitem /transaction type: 980
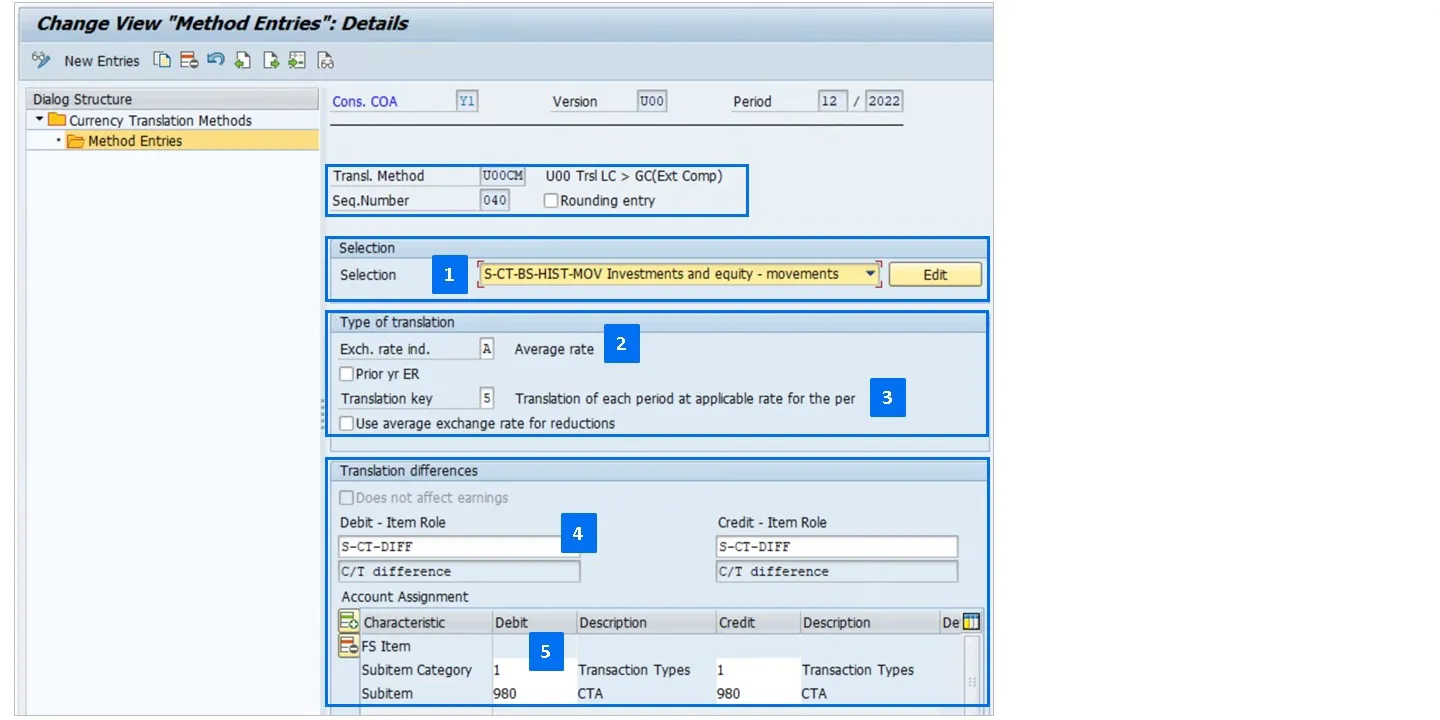
Historic Movements Translation
In the following image, the sequence to translate historical movements is configured:
• Select the source values for historical movements
• Use the average rate.
• Translate the period values at the period rates.
• Post translation differences to FS item 314800 (determined via FS item role S-CT-DIFF)
• Post currency translation adjustments to subitem /transaction type: 980
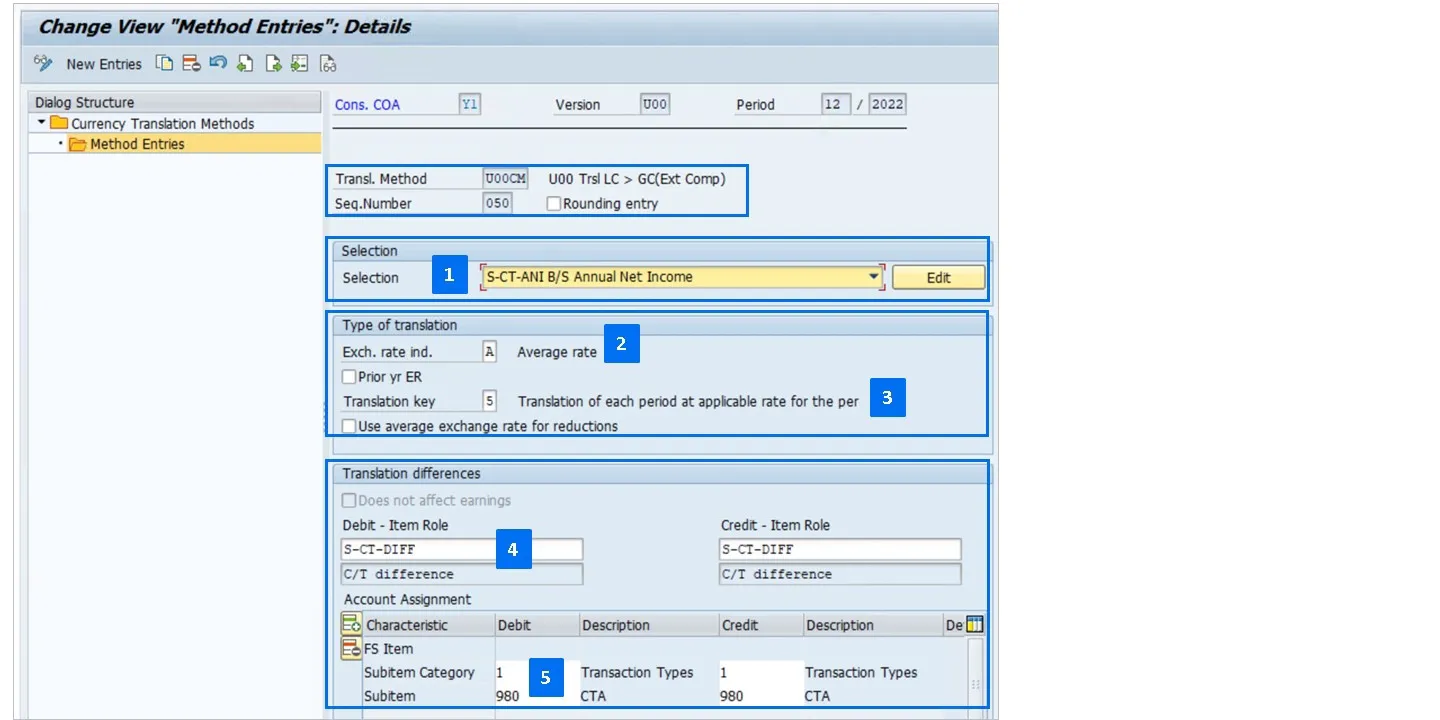
How does Current-Year Retained Earnings Translation happen?
In the following image, the sequence to translate retained earnings is configured:
• Select the source values for current-year retained earnings
• Use the average rate
• Translate the period values at the period rates
• Post translation differences to the FS item 314800 (determined via FS item role S-CT-DIFF)
• Post currency translation adjustments to subitem /transaction type: 980
After configuration of CT method, Assigning Translation Method to Consolidation Units
Fiori App: Define Consolidation Units
• Select consolidation unit.
• Assign translation method
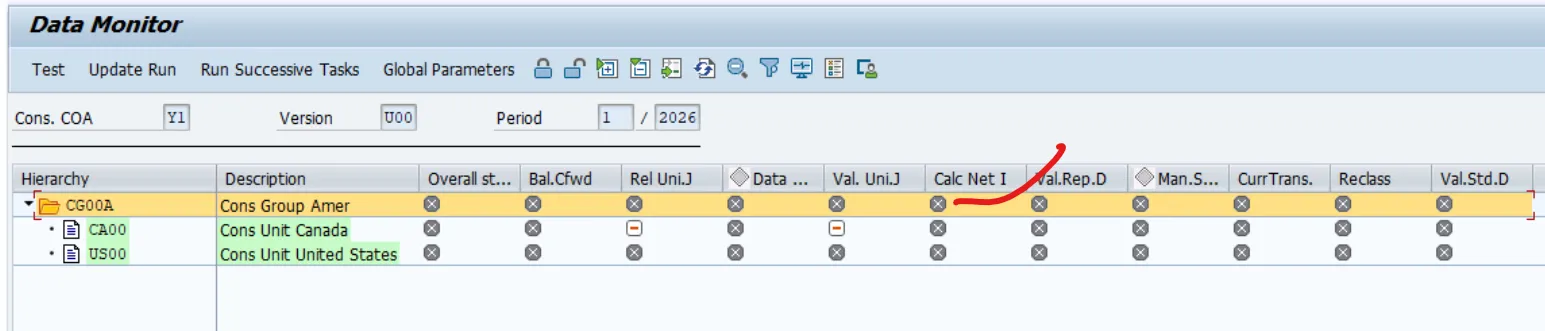
Run Annual Net Income Task (Precondition)
• Before executing CT, always run the Annual Net Income task to ensure retained earnings are correctly carried forward. This guarantees accurate closing balances for translation.
Fiori App: Consolidation Monitor → Annual Net Income
Execute Currency Translation Task
Fiori App: Consolidation Monitor → Currency Translation
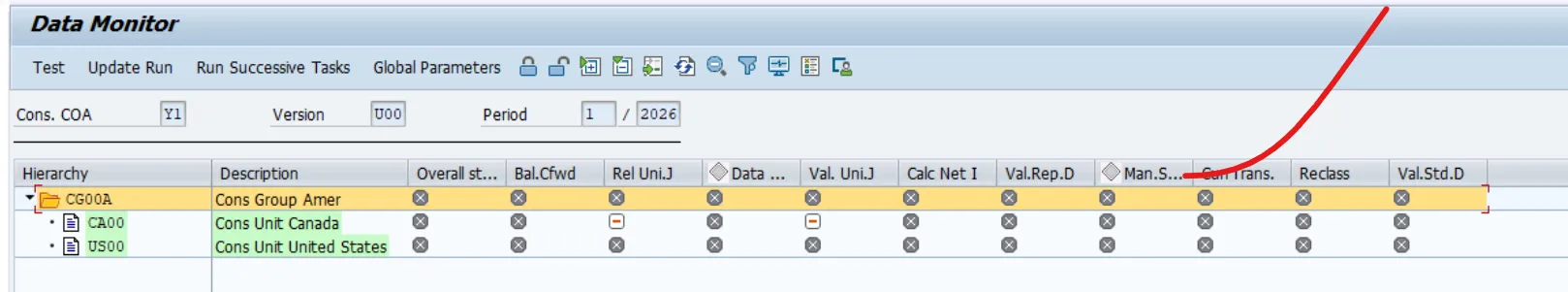
• Open the Consolidation Monitor.
• Select the Currency Translation task.
• Execute translation for the chosen period.
• System translates LC → GC based on assigned methods and exchange rates.
• Review logs for errors or exceptions (e.g., missing rates).
• Check postings in ACDOCU (Consolidation Journal).
• Validate translated balances against source data.
• Drill down to Universal Journal entries for auditability.
• Translated values are posted into Group Reporting tables (ACDOCU).
• Use Data Monitor and Consolidation Monitor to validate:
Below are the Best Practices for Consultants
• Always maintain exchange rates before closing to avoid CT task failures.
• Align FS item categories with correct translation logic (CLO vs AVG vs HIST).
• Use simulation runs (AVG2/CLO2) for testing before actual close.
• Leverage parallel ledgers for multi-GAAP reporting.
• Document CT configuration for auditors and finance controllers.
• Maintain exchange rates regularly to avoid missing values during CT.
• Align FS item categories with correct translation logic (closing vs average).
• Use simulation runs (AVG2/CLO2) to test translation before actual close.
• Leverage parallel ledgers for multi-GAAP reporting.
• Integrate with SAP Analytics Cloud for visualization of translated results.
Below are the Risks & Considerations
• Incorrect rate assignment can distort consolidated results.
• Skipping Annual Net Income task leads to misstatements in retained earnings.
• Incomplete exchange rate maintenance causes CT task failures.
• Multiple group currencies require careful setup to avoid duplication or inconsistencies.
Sources:
SAP Help Portal – Currency Translation (Cloud) :
SAP Help Portal – Currency Translation (On-Premises)